Economics has created the baseline for most decision-making processes. It uses tools and theories to analyze resources and given factors to understand an issue and come to a decision that would benefit an organization. One such tool is game theory, which is extensively used in economics and business management to analyze situations, decisions, and scenarios and predict potential outcomes. In this article, we will discuss the elements of game theory, its different types, and how it helps businesses make informed decisions.
We will also discuss how learning about game theory is an important aspect when it comes to getting a career in the mathematics or economics industry.

What Signifies Game Theory?
Game theory was originally created as a mathematical framework by mathematicians John von Neumann, John Nash, and economist Oskar Morgenstern. While it was originally designed for mathematical problems, its use has been extended over the years to various fields such as management economics, bio-sciences, and social sciences.
Game theory mathematically derives a player's decision based on the other player's decision.
In mathematical terms, it is described as deriving an optimal choice using a set of circumstances. If there is more than one player with a fixed number of decisions, you are more likely to find a known outcome.
Before we discuss the types of game theory and the importance of game theory when it comes to creating decision-making strategies, we need to understand the concept with an example in action.
Also, we would like to point out that we at Superprof have a team of experts that can teach students all they need to know about game theory and behavioral economic applications.

What Is An Example Of Game Theory?
An ideal example that explains the concept of game theory is the prisoner's dilemma.
While game theory is a vast subject with several different sub-branches, the prisoner's dilemma offers a complete explanation of what the theory is all about.
Consider the situation of two criminals that have been brought to the police station for questioning. They are under suspicion of robbing a bank, and the police want them to confess to their crime in order to convict them. To eliminate any chances of correspondence between the two criminals, they have confined them in different rooms. Each criminal is given four options;
- If both criminals confess, they will be sentenced to four years in prison
- If suspect 1 confesses but suspects 2 does not, then suspect 1 will only have to serve a one-year sentence while suspect 2 will need to serve a sentence of eight years
- If suspect 2 confesses while the other doesn't, then suspect 1 will serve an eight-year prison sentence, while suspect 2's ruling will be cut down to only a year
- If neither of the suspects confesses, they will each serve a prison sentence of two years
Considering these options, it is clear that not confessing to the crime is the best-case scenario for both suspects. Neither have a chance to discuss the possibilities with the other. We can automatically assume that the suspects will choose options that result in the lowest prison sentence. While they make the best decision for themselves individually and not collectively, it can result in a greater prison sentence for both.
This is an example of non-cooperative game theory. We will discuss this type of game theory in further detail later in the article.
To give a general explanation, non-cooperative game theory pertains to players' decisions being mutually exclusive. While the impact may be on all players, they will only choose a decision that benefits them.
While game theory has several real-world applications, the grassroots of this framework stems from economics and mathematics. Both these subjects can play a vital role in your career moving forward. If you want to learn game theory from an expert, Superprof has expert teachers that can help you understand the importance of game theory to hone your skills and propel you in your career.
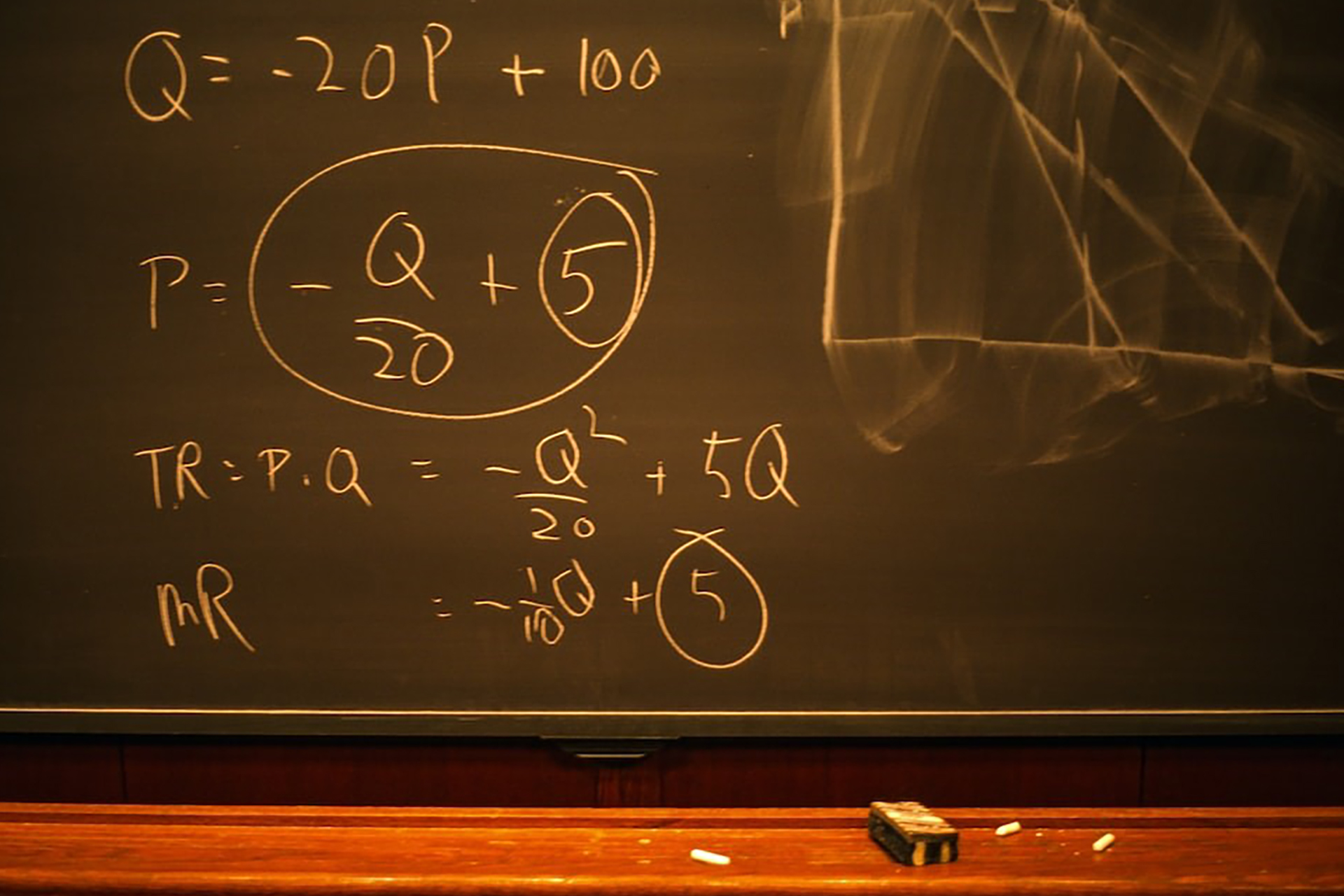

What Are The Two Types Of Games In Game Theory?
Game theory is divided into two types; cooperative and non-cooperative, each with a specific application of game theory.
Cooperative Game Theory
CGT or Cooperative Game Theory is a subclass of game theory where the participants, otherwise known as players, in the competition have to work together in cooperation with an external factor. The cooperative behavior of the players is tracked by an external force such as a contract or set of rules. In simple terms, it is similar to any team sport where the actions of a single individual will impact the entire game/situation. It is also known as a Coalition game.
One aspect of cooperative games is known as transferrable utility. It is the ability to transfer advantage from one player to another without bearing any loss in the process. Consider the following examples.
Example 01 Two companies, A Ltd and B Ltd, work in the beverage industry and are looking to launch a new soda pop. Both companies are importing the flavor from overseas.
The payoff of this game is that the company introducing the product first becomes the pioneer in the industry as no brand has ever presented a product of this kind. The product needs to click in order to boost the profit line of the company.
The strategy requires companies to decide the quantity of flavor they need to import from overseas.
The external factors, in this case, are the import/export governing authorities. These authorities have placed restrictions on the quantity that can be imported into the country in one interval.
The companies can decide to collaborate and sign an agreement with each other. While working together, they will still be separate entities and import the same quantity each quarter to ensure they comply with quote restrictions.
While this is a simple scenario with a single external factor and an apparent solution, real-world examples have an "n" number of possibilities, external factors, and strategies.
It results in several different combinations, each with its own results.
What is Non-Cooperative Game Theory?
While cooperative game theory promotes coalition, non-cooperative game theory expects the individual or participant to take actions that are only profitable to them. The reason is that, unlike the cooperative approach, there are no external factors that influence the decisions taken by the player.
This type of game theory can be understood with the prisoner dilemma. Each player is looking for the best payoff for themselves and not considering the best payout option collaboratively.
While cooperative game theory is about the coalition, non-cooperative is known for dominance. Dominance theory expects the player to aim for the most favorable outcome irrespective of the repercussion or strategy of the other player.
Nonetheless, non-cooperative game theory has certain limitations associated with it, such as;
- Ties
- Lack of complete information
- Backward induction
Game theory plays an integral part in several jobs, such as economics and business analysis. These jobs can provide you with a high and stable income. Superprof has a team of experts that will teach you all the aspects of game theory and how you can master this framework to improve your career path.
Join an economic lessons for elementary here on Superprof.
Nash Equilibrium
Josh Nash was a famous mathematician and has contributed to the community several times. One of his most notable contributions was the Nash Equilibrium. The theory suggests that there are instances where outcomes can reach equilibrium when the player cannot improve the results in any way by making a decision. This framework specifically pertains to non-cooperative games.
The famous movie 'A Beautiful Mind' is based on John Nash's life. The film shows the mathematician coming up with the idea of the theory when he sees all his friends flirting with the most beautiful girls around them. He observed that the probability of getting accepted lay in approaching the crowd's second or third most attractive girl.
Why Is Game Theory Important?
There are practical applications of game theory in several fields. Following are some of the examples that can help with real-world scenarios;
- Economists use game theory to analyze the actions of firms trading in oligopolies. These firms, such as OPEC, are treated as players according to the game theory. It allows them to understand the decision-making process with regard to setting prices, mergers, and any potential price wars. Moreover, the theory enables economists to predict the outcomes
- Game theory assists businesses in making strategic decisions on aspects such as retiring a product or launching a new one
- The game theory also allows the business analyst to determine the market equilibrium in a scenario when there is more than one competition
Game theory in economics and mathematics is making waves within the sector. Several experts believe that applying game theory is helpful in several jobs, such as business analysis and even crypto analysis, if we consider the current times. Learning about game theory in economics and other disciplines can help you excel in your career.
Superprof has a team of experts that can teach you all you need to know about game theory. We will offer classes on game theory to simplify your path to understanding the topic and applying it in real-world situations.
Want To Learn More About Game Theory With Superprof?
Game theory can help you excel in economics and relevant fields such as mathematics, business, statistics, and finance. It is an all-encompassing study that refines an individual's ability to excel in several areas. A thorough understanding and expertise in game theory can land you the following jobs/professions;
| Job | Salary |
|---|---|
| Economist | $116,000 |
| Business Analyst | $75,000 |
| Finance Analyst | $83,000 |
| Blockchain Analyst | $114,000 |
Superprof features many talented economics and mathematics tutors who can help you learn game theory and advance your career in economics, finance, and management. Visit Superprof to hire a game theory expert and let the learning begin!
Summarize with AI:















