Chapters

Division of a Polynomial By a Number
When we divide a polynomial by a number, the result is another polynomial that fulfills the following characteristics:
- The resulting polynomial has the same degree as the polynomial that was divided.
- Its coefficients result from dividing each of the coefficients of the polynomial by the number.
- The same literal parts are kept.
Examples:






Division of a Polynomial By a Monomial
In the division of a polynomial by a monomial, each of the monomials that form the polynomial is divided by the monomial, until the degree of the dividend is less than the degree of the divisor.
Examples:
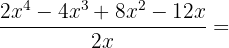
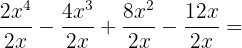
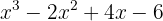
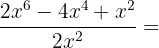

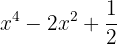
Division of a Polynomial By a Polynomial
To explain polynomial division we will use a practical example with the polynomials:



On the left we place the dividend. If the polynomial is not complete we leave gaps in the corresponding places, that is, in this case we leave space for the fourth-degree element and another space for the second-degree element.
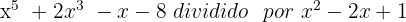
On the right we place the divisor inside a box.
We divide the first monomial of the dividend by the first monomial of the divisor.

We multiply each term of the divisor polynomial by the previous result and subtract it from the dividend polynomial:
That is: 
Remember that it will be subtracted from the polynomial, so we must place it with the opposite sign:


We divide again the first monomial of the dividend by the first monomial of the divisor.

And we multiply the result by the divisor and subtract it from the dividend.

Remember that it will be subtracted from the polynomial, so we must place it with the opposite sign:


We proceed as before.

And we multiply the result by the divisor and subtract it from the dividend.

Remember that it will be subtracted from the polynomial, so we must place it with the opposite sign:


We perform the same operations again.

And we multiply the result by the divisor and subtract it from the dividend.

Remember that it will be subtracted from the polynomial, so we must place it with the opposite sign:


The division concludes here, since  has a lower degree than the divisor.
has a lower degree than the divisor.
Quotient or result of the division: 
Remainder or residue: 
Summarize with AI:












