Chapters

What are exponential equations?
Exponential equations are those in which the variable is found in the exponent of a number.
For example:

Where  and
and  are constants
are constants
To solve exponential equations, in general, we will encounter two cases: equations whose members can be expressed in a single base and equations whose members CANNOT be expressed in a single base. Although there are exponential equations in which we must use some mathematical trick to solve them.
Equations Whose Members Can Be Expressed in a Single Base
To solve this type of equation we will express the two members of the equation in terms of the same base and then equate the exponents. Finally, we solve the equation obtained by equating the exponents
Equations Whose Members CANNOT Be Expressed in a Single Base
To solve these equations, we will use logarithms and their properties so that the unknown does not remain in the power and then we will solve the resulting equation
Other Types of Exponential Equations
There are exponential equations in which we must use some mathematical tricks to be able to isolate the variable
Exercises on Exponential Equations Whose Members Can Be Expressed in a Single Base
Solve the following exponential equations:

1 Since the number  can be written as
can be written as 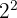 , we can rewrite the equation as:
, we can rewrite the equation as:

2 Since we have base  in both members of the equation, we can equate the powers
in both members of the equation, we can equate the powers

3 We solve the first-degree equation that resulted




1 We transform the roots into powers with fractional exponents and equate the exponents


2 We solve the resulting equation





1 We rewrite  as
as  and equate the exponents
and equate the exponents


2 We solve the resulting equation



1 We rewrite the root in the form of a power with fractional exponent and  is factored
is factored




1 We transform the fraction on the right

2 We equate exponents and solve the resulting equation





1 We transform the roots into powers with fractional exponents and equate the exponents


2 We solve the resulting equation




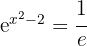
1 We rewrite the fraction on the right

2 We equate exponents and solve the resulting equation





1 We rewrite the fraction on the right side and write the square root as a fractional exponent

2 We equate exponents and solve the resulting equation





1 We factor  and
and  and equate the exponents
and equate the exponents



2 The resulting equation can be simplified and then solved





1 We move the second term to the right, factor  and equate the exponents
and equate the exponents


2 We solve the irrational equation we obtained

Exercises on Exponential Equations Whose Members CANNOT Be Expressed in a Single Base
Solve the following exponential equations:

1 Since we have different bases, we apply logarithms to both members

2 We apply the property of the logarithm of a power in the first member

3 We move  to the other member and solve the equation
to the other member and solve the equation




1 We can rewrite the equation as

2 We move  to the first member and
to the first member and  to the second member
to the second member


3 We apply logarithms to both members

4 We apply the property of the logarithm of a power in the first member and solve the resulting equation



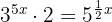
1 We can rewrite the equation as

2 We move  to the first member and
to the first member and  to the second member
to the second member


3 We apply logarithms to both members
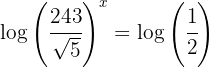
4 We apply the property of the logarithm of a power in the first member and solve the resulting equation

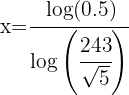


1 We apply logarithms to both members

2 We apply the property of the logarithm of a power in the first member and solve the resulting equation





1 We apply logarithms to both members and apply the property of the logarithm of a product in the first member
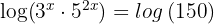

2 We apply the property of the logarithm of a power and factor out 


3 We isolate the unknown and solve the operations with the logarithms


Exercises on Exponential Equations Using Mathematical Tricks
Solve the following exponential equations:

1 We apply the property of the power of a product and quotient, to remove the addition or subtraction from the exponents

2 We extract 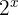 as a common factor
as a common factor

3 We isolate 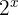 and express both members with base
and express both members with base 



4 We equate the exponents


1 We apply the property of the power of a quotient, to remove the subtraction from the exponent

2 We make a change of variable and substitute into the equation


3 By multiplying both members of the equation by  and moving all terms to the first member we obtain
and moving all terms to the first member we obtain

4 By solving the quadratic equation we would obtain
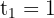

5 We substitute the values of  in
in 
 ...
... 
 ...
... 
6 Equation  has no solution, since a power with a positive base cannot give a negative number, so we only solve equation
has no solution, since a power with a positive base cannot give a negative number, so we only solve equation 


1 We apply the properties of powers of a product or quotient, to remove the additions or subtractions from the exponents

2 We make the change of variable  and substitute it into the equation
and substitute it into the equation

3 We multiply both members by  and solve the resulting equation
and solve the resulting equation



 Has no solution
Has no solution





1 We factor  , apply the properties of the product and quotient of powers to remove the additions and subtractions from the exponents
, apply the properties of the product and quotient of powers to remove the additions and subtractions from the exponents


2 We make the change of variable  and solve the resulting equation
and solve the resulting equation




3 We return to the original variable and verify if the solutions are valid
 Has no solution
Has no solution




1 We factor  and
and 

2 We make the change of variable  and solve the resulting equation
and solve the resulting equation



3 We undo the change of variable only with the positive solution.

4 Since we cannot equate exponents we take logarithms on both members and in the first member we apply the property of the power


5 We isolate the variable 


6 For the negative solution of the quadratic equation we would not obtain a solution for our exponential equation since by applying logarithms in the second member we would encounter the logarithm of a negative number, which does not exist.
 Has no solution
Has no solution

1 We remove negative exponents by taking the reciprocal

2 We clear denominators by multiplying by 

3 We make the change of variable  and solve the resulting equation
and solve the resulting equation

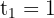

4 We return to the original variable and solve for 









1 We make the change of variable 

2 We solve the equation and undo the change of variable





 Has no solution
Has no solution

1 We apply the formula for the sum of  terms of a geometric progression
terms of a geometric progression

2 We isolate 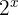
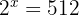
3 We rewrite  as
as  and equate the powers
and equate the powers



1 We apply the formula for the sum of  terms of a geometric progression
terms of a geometric progression

2 We put the terms with a common denominator

3 We clear denominators and solve the resulting equation





1 We cube both sides of the equation to maintain equality

2 We use the properties of exponents and rewrite the equation. We use that 

3 Again, we use the properties of exponents and rewrite the equation
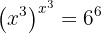
4 Therefore we have that

5 Finally, we have that

Summarize with AI:












