Chapters
When we talk about factoring polynomials, there are several characteristics we need to take into account.

If There Is No Independent Term
If there is no independent term, we must factor out the common factor. Factoring out the common factor from a sum (or difference) consists of transforming it into a product.
We would apply the distributive property:
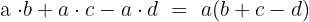
Example of Polynomial Factorization Without Independent Term
Factor out the common factor and find the roots.
1 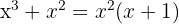
The roots are:  y
y 
2 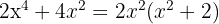
It only has one root  because the polynomial
because the polynomial  has no value that makes it zero. Since
has no value that makes it zero. Since  is squared, the result will always be a positive number, so it is irreducible.
is squared, the result will always be a positive number, so it is irreducible.
Double Extraction of Common Factor
1 
We factor out  and
and  .
.
Since  is now a common factor, we factor out
is now a common factor, we factor out  .
.

The roots are  and
and  .
.
If We Have a Binomial
When we have a binomial, one of the following cases may occur:
Difference of Squares
A difference of squares equals the product of sum and difference.

Examples of Exercises with Difference of Squares:
Factor and find the roots:
1 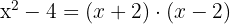
The roots are  and
and 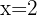
2 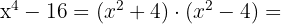
The last term is also a difference of squares, so:
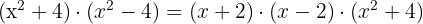
The roots are  and
and 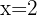
Sum of Cubes
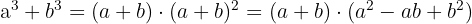
Example of Exercise with Sum of Cubes:

Difference of Cubes
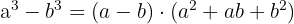
Example of Exercise with Difference of Cubes:
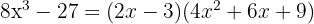
If We Have a Trinomial
When we have a trinomial, one of the following cases may occur:
Perfect Square Trinomial
A perfect square trinomial equals a binomial squared.
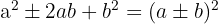
Examples of Perfect Square Trinomials
Factor and find the roots:
1 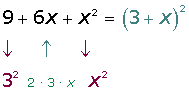
We have to ask ourselves:
- What number squared gives
 ? The answer is
? The answer is  .
. - What number squared gives
 ? The answer is
? The answer is  .
.
And we have to verify that 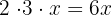
The root is  , and it is called a double root.
, and it is called a double root.
2 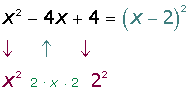
- What number squared gives
 ?
? 
- What number squared gives
 ?
? 
And we have to verify that 
The double root is  .
.
Quadratic Trinomial
To factor the quadratic trinomial 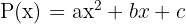 , we set it equal to zero and solve the quadratic equation.
, we set it equal to zero and solve the quadratic equation.
If the solutions to the equation are y , the factored polynomial will be:

Examples of Quadratic Trinomials
Factor and find the roots
1
We set the trinomial equal to zero:

We apply the quadratic formula:
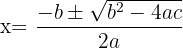
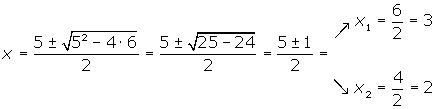
We factor
The roots are  and
and 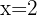 .
.
2
We set the trinomial equal to zero:

We solve the equation:
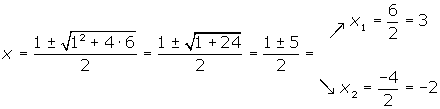
We factor:
The roots are  and
and  .
.
Fourth-Degree Trinomials with Even Exponents
To find the roots, we set it equal to zero and solve the biquadratic equation.
Examples of Fourth-Degree Trinomials with Even Exponents
1 
We set the polynomial equal to zero:
We make a substitution:
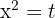
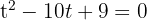
We solve the quadratic equation:
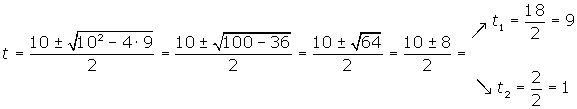
We undo the substitution and obtain the roots:
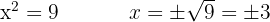

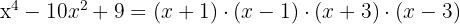
2 
We set the polynomial equal to zero:

We make a substitution:
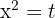
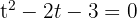
We solve the quadratic equation:
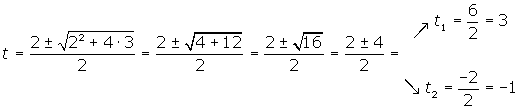
We undo the substitution and obtain the roots:

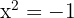 has no real roots, since there is no number that squared is negative.
has no real roots, since there is no number that squared is negative.
It factors as 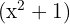
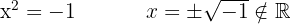
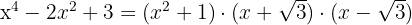
Factorization of a Polynomial of Degree Greater Than Two
We use the remainder theorem and Ruffini's rule to find the integer roots.
The steps to follow are shown with the polynomial:

We take the divisors of the independent term:  .
.
Applying the remainder theorem, we will know for which values the division is exact.
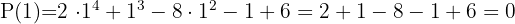
We divide using Ruffini.
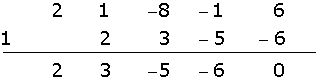
Since the division is exact, 
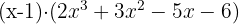
One root is  .
.
We continue performing the same operations to find the second factor.
We try  again because the first factor could be squared.
again because the first factor could be squared.

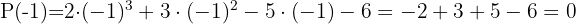
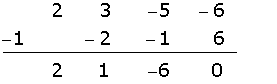

Another root is  .
.
The third factor can be found by applying the quadratic equation or as we have been doing, although it has the disadvantage that we can only find integer roots.
We discard  and continue testing with
and continue testing with  .
.
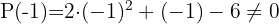
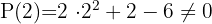

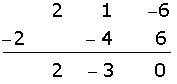
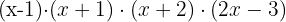
We factor out  from the last binomial and find a rational root.
from the last binomial and find a rational root.
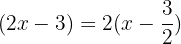
The factorization of the polynomial is:
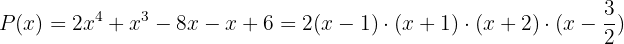

Rational Roots
It may happen that the polynomial has no integer roots and only has rational roots. In this case, we take the divisors of the independent term divided by the divisors of the highest degree term, and apply the remainder theorem and Ruffini's rule.

We try:
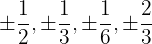 .
.

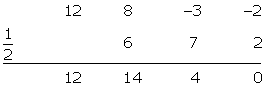
We factor: 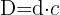
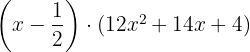
We try again for: 

We try for: 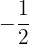
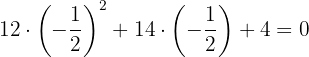
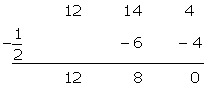
We factor: 
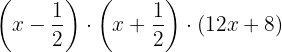
We factor out  from the third factor.
from the third factor.
Find the perfect math tutor for you, only at Superprof!
Summarize with AI:












