Chapters

Definition of the Inverse of a Matrix
A square matrix  is said to be invertible if there exists a matrix
is said to be invertible if there exists a matrix  with the property that
with the property that 
where  is the identity matrix.
is the identity matrix.
The matrix  is unique, we call it the inverse of
is unique, we call it the inverse of  and denote it by
and denote it by  That is,
That is, 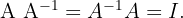
Important observation: A matrix is invertible if and only if its determinant is different from zero. That is, a matrix has an inverse if its determinant is non-zero.
Properties of the Inverse Matrix
The inverse of a matrix satisfies the following properties:
1 Let  and
and  be invertible matrices of the same order, then the product
be invertible matrices of the same order, then the product 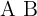 is invertible and furthermore
is invertible and furthermore 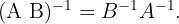
2 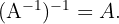
3 Let  be a non-zero real number, then
be a non-zero real number, then 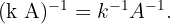
4 If 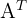 denotes the transpose of a matrix, then
denotes the transpose of a matrix, then 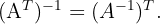
- The inverse matrix is an important tool in solving systems of linear equations since any system can be written in the form
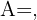 where
where  is the coefficient matrix of the system,
is the coefficient matrix of the system,  is the column matrix or column vector that contains the "unknown" variables and
is the column matrix or column vector that contains the "unknown" variables and  is the column matrix whose entries are the constants on the right side of the equations in the system. For example, the system
is the column matrix whose entries are the constants on the right side of the equations in the system. For example, the system
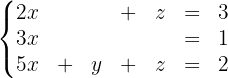
can be expressed as the matrix equation 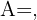 where
where
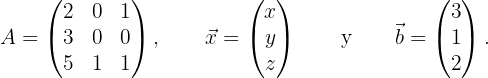
Since the coefficient matrix  is square, it may be invertible.
is square, it may be invertible.
If  is invertible and we have a way to calculate its inverse
is invertible and we have a way to calculate its inverse 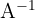 , then we can determine
, then we can determine  by simply a matrix multiplication:
by simply a matrix multiplication: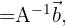
since 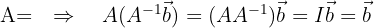
solving the system of equations.
Thus, a good application of the inverse of a matrix is the efficient solution of systems of linear equations.
Let's recall that, the transpose matrix of a matrix  is denoted by
is denoted by 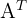 and is obtained by exchanging its rows for columns (or vice versa).
and is obtained by exchanging its rows for columns (or vice versa).
For example, continuing with the matrix  from above we have that, if
from above we have that, if

The inverse matrix can be calculated by two methods: by the Gauss method and by the adjoint method. In the latter is where the transpose matrix appears. Thus, the main practical application of the transpose matrix is the calculation of the inverse matrix.
We have already studied the Gauss method in another article, now we will focus our attention on the adjoint method.
Calculation by the Adjoint Method
The calculation of an inverse matrix by the adjoint method is based on the following result:
Where

To understand the procedure, let's look at an example:
Example: Calculate the inverse of the matrix
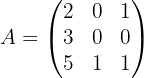
which corresponds to the coefficients of the system of linear equations from above.
Solution:
To calculate the inverse we must follow these steps:
1 We calculate the determinant of the matrix:
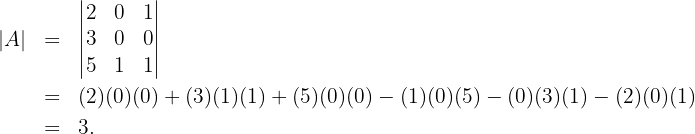
Since the determinant is not zero, the matrix has an inverse.
2 We find the adjoint matrix: This is the one in which each element is replaced by its adjoint.
That is,
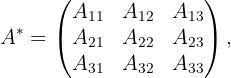
where 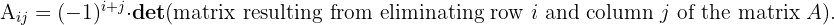
Thus

Therefore we have that

3 We calculate the transpose of the adjoint matrix: If

4 The inverse matrix equals the transpose of the adjoint matrix divided by the determinant of the original matrix: That is,

Therefore
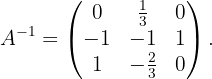
Thus, we have obtained the inverse of the matrix  .
.
Observation: As a final comment, we can solve the previously stated system of linear equations by doing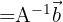
obtaining that
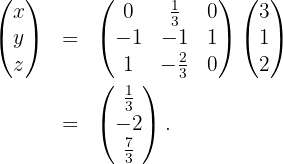
Then, the choice of 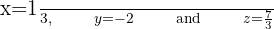
solves the previously stated system, as can be easily verified.
Summarize with AI:












