Logarithmic equations are fundamental in the study of mathematics, as they allow solving problems in various fields, from science to economics. A logarithm, in simple terms, answers the question: "To what exponent must we raise a base to obtain a given number?" This relationship converts multiplications into additions, facilitating the resolution of complex equations.
Solve the following logarithmic equations:
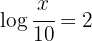
1 In the first member we apply the property of the logarithm of a quotient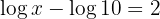
2 Taking into account that 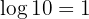
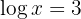
3 Taking into account the definition of logarithm and that it is a common logarithm: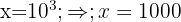
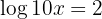
1 In the first member we apply the property of the logarithm of a product
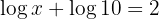
2 Taking into account that 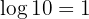
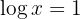
3 Taking into account the definition of logarithm and that it is a common logarithm:
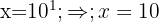
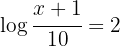
1 In the first member we apply the property of the logarithm of a quotient
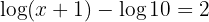
2 Taking into account that 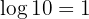
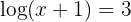
3 Taking into account the definition of logarithm and that it is a common logarithm:
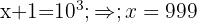
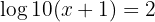
1 In the first member we apply the property of the logarithm of a product
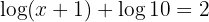
2 Taking into account that 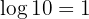
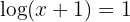
3 Taking into account the definition of logarithm and that it is a common logarithm:
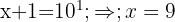
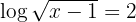
1 In the first member we write the root as a fractional power and apply the property of the logarithm of a power
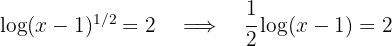
2 We solve for the logarithm
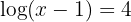
3 Taking into account the definition of logarithm and that it is a common logarithm:
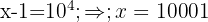
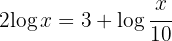
1 In the second member we apply the property of the logarithm of a quotient
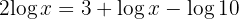
2 We subtract  from both members and taking into account that
from both members and taking into account that 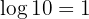 , we have:
, we have:
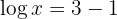
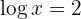
3 Taking into account the definition of logarithm and that it is a common logarithm:
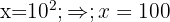
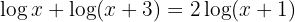
1 In the first member, we apply the property of the sum of logarithms:
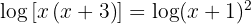
2 Taking into account the injectivity of logarithms (or equating the arguments) we have:

3 We solve the equation and check the solution
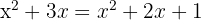


1 We apply the property of the logarithm of a power in both members
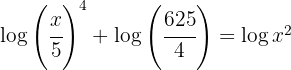
2 We apply the property of the logarithm of a product
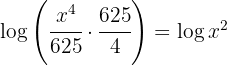
3 We perform operations in the first member

4 We apply the injectivity of logarithms to remove logarithms
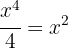
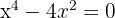
5 We solve the equation
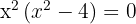
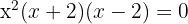
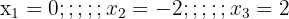
6 Neither  nor
nor  are solutions because if we substitute them in the equation we encounter logarithm of 0 and logarithm of a negative number and such logarithms do not exist, so the only solution is
are solutions because if we substitute them in the equation we encounter logarithm of 0 and logarithm of a negative number and such logarithms do not exist, so the only solution is 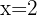
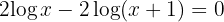
1 We move 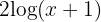 to the second member and apply the power property in both members
to the second member and apply the power property in both members
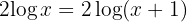

2 We apply the injective property and find the values of 
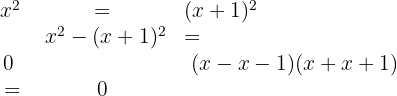
3 Solving the first factor we obtain 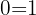 , which is an inconsistency and means the equation has no solution. Solving the second factor we have
, which is an inconsistency and means the equation has no solution. Solving the second factor we have 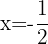 , but
, but  is not defined and means the equation has no solution.
is not defined and means the equation has no solution.

1 We clear denominators and make a change of variable
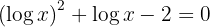
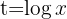
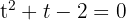
2 Solving the equation
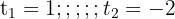
3 We undo the change of variable and apply the definition of logarithm
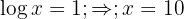
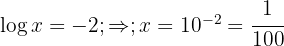

1 We move the second term to the 2nd member and apply the property of the logarithm of a power
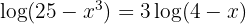

2 We apply the injectivity of logarithms and develop the operations
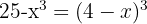
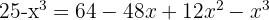
3 We solve the equation applying the quadratic formula

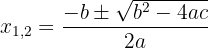
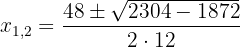
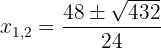
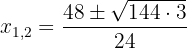
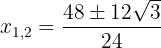
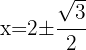

1 We multiply both members by 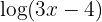
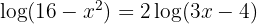
2 In the second member we apply the property of the logarithm of a power and take into account the injectivity of logarithms

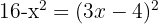
3 We solve the equation,  is not a solution because we would encounter the logarithm of a negative number in the denominator when substituting in the equation.
is not a solution because we would encounter the logarithm of a negative number in the denominator when substituting in the equation.

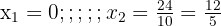
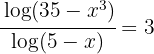
1 We clear denominators
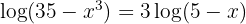
2 In the second member we apply the property of the logarithm of a power and subsequently apply the injectivity of logarithms
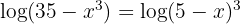
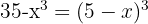
3 We perform the operations and solve the quadratic equation

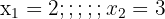
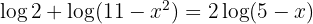
1 In the first member we apply the logarithm of a product and in the second the property of the logarithm of a power.
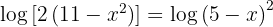
2 Taking into account the injectivity of logarithms we have:
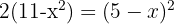
3 We solve the equation and verify that we do not obtain a zero or negative logarithm
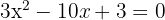


1 We multiply both members by 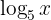 and move everything to the first member
and move everything to the first member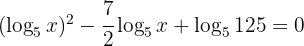
2 Considering that  and clearing denominators:
and clearing denominators:
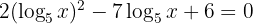
3 We make a change of variable
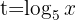
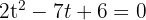
3 We solve the equation

4 We undo the change of variable
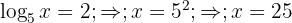
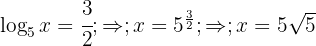
Summarize with AI:


