Paolo Ruffini (1765-1822) was an Italian mathematician who established a shorter method for dividing polynomials when the divisor is a binomial of the form x - a.

Ruffini's Rule
To explain the steps to apply in Ruffini's rule, we will take two examples:
First Example of Ruffini's Rule
Divide: 
1. If the polynomial is not complete, we complete it by adding the missing terms with zeros.
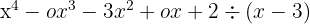
2. We place the coefficients of the dividend in a line.

3. Below on the left, we place the opposite of the independent term of the divisor: 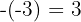 .
.


4. We draw a line and bring down the first coefficient  .
.
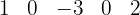
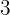

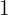
5. We multiply that coefficient  by the divisor
by the divisor 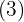 and place it below the next term
and place it below the next term 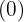 .
.
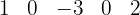


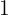
6. We add the two coefficients 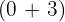 .
.
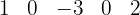



7. We repeat the previous process: 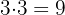 and
and 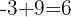 .
.
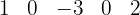



We repeat the process again: 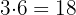 and
and 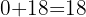 .
.
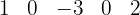


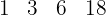
We repeat again:  and
and 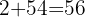 .
.
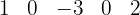



8. The last number obtained, 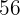 , is the remainder.
, is the remainder.
9. The quotient is a polynomial of degree one unit less than the dividend, and whose coefficients are those we have obtained.
Quotient: 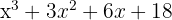
Remainder: 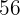
Second Example of Ruffini's Rule
Divide using Ruffini's rule: 
1. If the polynomial is not complete, we complete it by adding the missing terms with zeros.
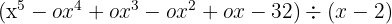
2. We place the coefficients of the dividend in a line.
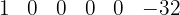
3. Below on the left, we place the opposite of the independent term of the divisor: 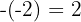 .
.


4. We draw a line and bring down the first coefficient  .
.



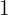
5. We multiply that coefficient  by the divisor
by the divisor  and place it below the next term
and place it below the next term 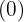 .
.



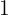
6. We add the two coefficients  .
.



7. We repeat steps  and
and  until the end.
until the end.


8. The quotient is a polynomial of degree one unit less than the dividend, and whose coefficients are those we have obtained.
Quotient:
Remainder: 
Summarize with AI:












