In this article, we'll solve linear programming exercises step by step. Remember that linear programming provides answers to situations where we need to maximize or minimize functions that are subject to certain limitations, which we call constraints. We'll apply this mathematical tool to solve optimization problems in areas such as industry, economics, and more.
A company manufactures and sells two models of lamps L1 and L2. For their production, manual work of 20 minutes is needed for model L1 and 30 minutes for L2; and machine work of 20 minutes for model L1 and 10 minutes for L2. There are 100 hours per month available for manual work and 80 hours per month for machine work. Knowing that the profit per unit is $15 and $10 for L1 and L2, respectively, plan the production to obtain maximum profit.
1 Choice of variables.
 = number of L1 lamps
= number of L1 lamps
 = number of L2 lamps
= number of L2 lamps
2 Objective function

3 Constraints
We convert the times to hours
20 min = 1/3 h
30 min = 1/2 h
10 min = 1/6 h
To write the constraints we'll use a table:
| L1 | L2 | Time | |
| Manual | 1/3 | 1/2 | 100 |
| Machine | 1/3 | 1/6 | 80 |
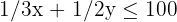

Since the number of lamps are natural numbers, we have two more constraints:
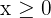

4 Find the feasible solution set
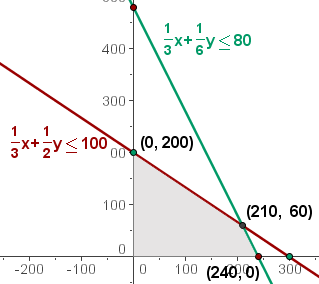
We need to graphically represent the constraints. Since 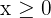 and
and  , we work in the first quadrant. We represent the lines from their intersection points with the axes.
, we work in the first quadrant. We represent the lines from their intersection points with the axes.
We solve graphically the inequality: 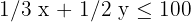 ; for this, we take a point on the plane, for example
; for this, we take a point on the plane, for example  .
.


The intersection zone of the inequality solutions would be the solution to the system of inequalities, which constitutes the set of feasible solutions.
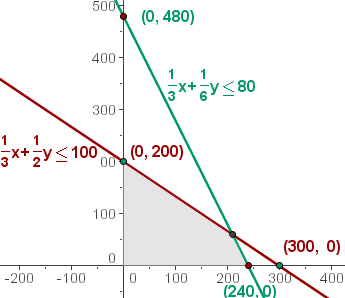
5 Calculate the coordinates of the vertices of the feasible solution region.
The optimal solution, if unique, is found at a vertex of the region. These are the solutions to the systems:
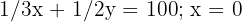
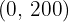
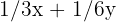
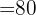 ;
; 
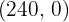
 ;
; 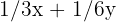
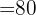

6 Calculate the value of the objective function
In the objective function we substitute each of the vertices.
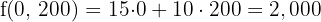
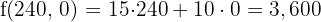
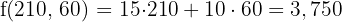 Maximum
Maximum
The optimal solution is to manufacture 210 of model L1 and 60 of model L2 to obtain a profit of $3,750.
With the start of the school year, school supply offers will be launched. Some warehouses want to offer 600 notebooks, 500 folders and 400 pens for the offer, packaging them in two different ways; in the first package they will put 2 notebooks, 1 folder and 2 pens; in the second, they will put 3 notebooks, 1 folder and 1 pen. The prices of each package will be $6.5 and $7, respectively. How many packages of each type should they make to obtain maximum profit?
1 Choice of variables.


2 Objective function
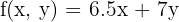
3 Constraints
| P1 | P2 | Available | |
| Notebooks | 2 | 3 | 600 |
| Folders | 1 | 1 | 500 |
| Pens | 2 | 1 | 400 |

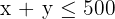

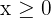
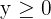
4 Find the feasible solution set
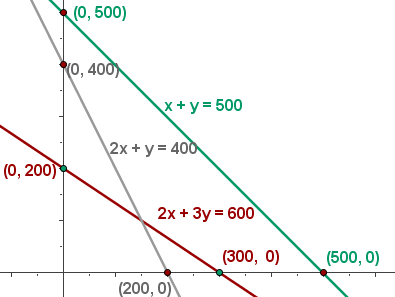
5 Calculate the coordinates of the vertices of the feasible solution region.
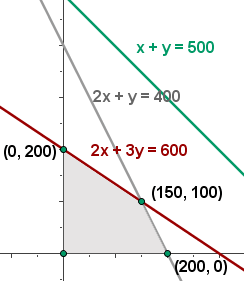
6 Calculate the value of the objective function


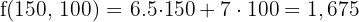 Maximum
Maximum
The optimal solution is 150 P1 and 100 P2 with which $1,675 is obtained.
On a chicken farm, a fattening diet is given with a minimum composition of 15 units of substance A and another 15 of substance B. In the market, only two types of compounds are found: type X with a composition of one unit of A and 5 of B, and the other type, Y, with a composition of five units of A and one of B. The price of type X is $10 and type Y is $30. What quantities should be bought of each type to cover the needs with minimum cost?
1 Choice of variables.
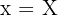

2 Objective function
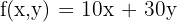
3 Constraints
| X | Y | Minimum | |
| A | 1 | 5 | 15 |
| B | 5 | 1 | 15 |
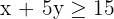

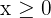

4 Find the feasible solution set
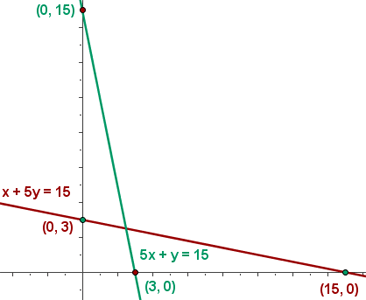
5 Calculate the coordinates of the vertices of the feasible solution region.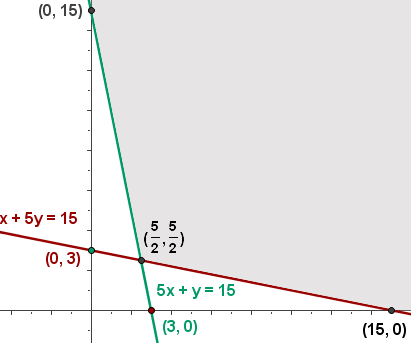
6 Calculate the value of the objective function

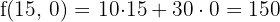
 Minimum
Minimum
The minimum cost is $100 for X=5/2 and Y=5/2.
There are 600 g of a certain drug available to make large and small pills. The large ones weigh 40 g and the small ones 30 g. At least three large pills are needed, and at least double the number of small pills as large ones. Each large pill provides a profit of $2 and the small one $1. How many pills of each type should be made for maximum profit?
1 Choice of variables.
 Number of large pills
Number of large pills
 Number of small pills
Number of small pills
2 Objective function

3 Constraints

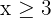

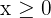

4 Find the feasible solution set
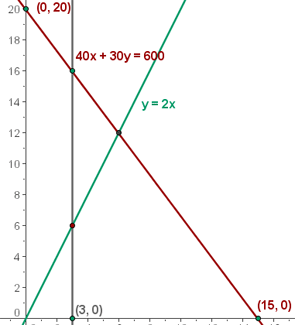
Review these concepts with private math classes.
5 Calculate the coordinates of the vertices of the feasible solution region.
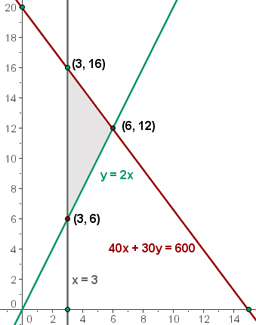
6 Calculate the value of the objective function

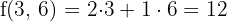
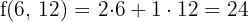 Maximum
Maximum
The maximum profit is $24, and it's obtained by manufacturing 6 large pills and 12 small pills.
A department store wants to liquidate 200 shirts and 100 pants from the previous season. To do this, they launch two offers, A and B. Offer A consists of a bundle of one shirt and one pair of pants, which sells for $30; offer B consists of a bundle of three shirts and one pair of pants, which sells for $50. They don't want to offer fewer than 20 bundles of offer A or fewer than 10 of B. How many bundles of each type should they sell to maximize profit?
1 Choice of variables.
 number of bundles of A
number of bundles of A
 number of bundles of B
number of bundles of B
2 Objective function

3 Constraints
| A | B | Available | |
| Shirts | 1 | 3 | 200 |
| Pants | 1 | 1 | 100 |

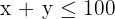


4 Find the feasible solution set
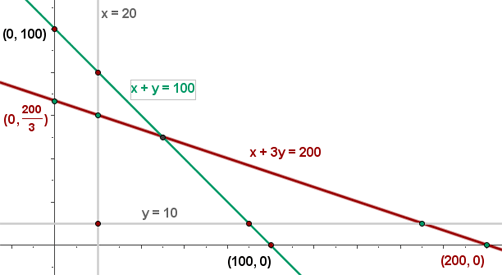
5 Calculate the coordinates of the vertices of the feasible solution region.
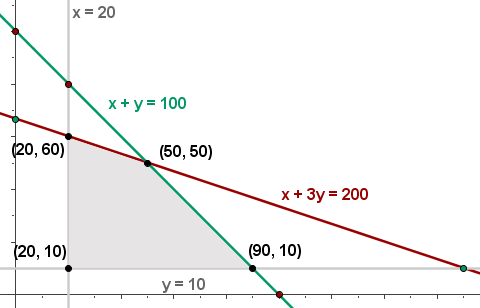
6 Calculate the value of the objective function
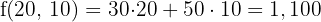
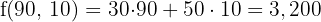
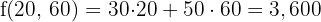
 Maximum
Maximum
With 50 bundles of each type, a maximum profit of $4,000 is obtained.
A company produces two types of calculator, model C1 and model C2. The manufacturing time for the calculators is 1 hour for model C1 and 4 hours for model C2. The manufacturing cost of model C1 is $30 and the cost of model C2 is $20. The company has 1600 hours available to manufacture the calculators and $18,000 for viable expenses. The profit on each calculator of model C1 is $10 and the profit for model C2 is $8. What should be the production plan to guarantee maximum profit?
1 Choice of variables.
 number of C1 calculators
number of C1 calculators
 number of C2 calculators
number of C2 calculators
2 Objective function

3 Constraints
| C1 | C2 | Available | |
| Hours | 1 | 4 | 1600 |
| Expenses | 30 | 20 | 18000 |
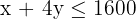

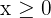

4 Find the feasible solution set
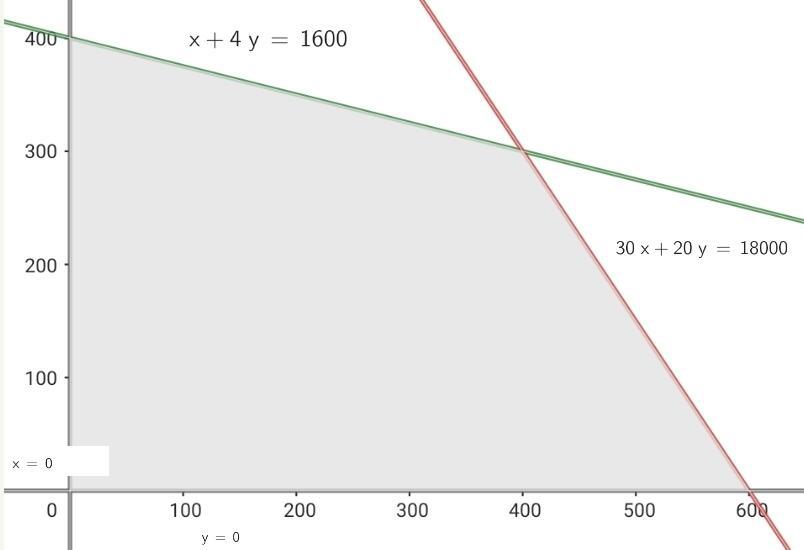
5 Calculate the coordinates of the vertices of the feasible solution region.
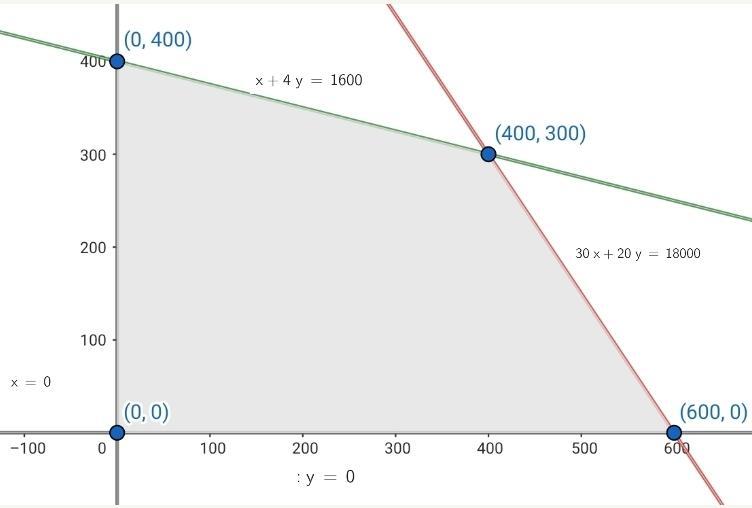
The vertices are: 
6 Calculate the value of the objective function
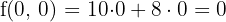

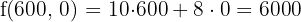
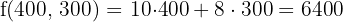 Maximum
Maximum
With 400 calculators of model C1 and 300 calculators of model C2, the maximum profit of $6,400 is obtained.
A businessman wants to sell 400 tables and 200 chairs. Two promotions are offered, 1 and 2. Promotion 1 consists of 1 table and 1 chair, which sell for $60; promotion 2 consists of 3 tables and 1 chair, which sell for $100. They don't want to offer fewer than 40 promotions of offer 1 or fewer than 20 promotions of offer 2. How many units should the company produce to maximize sales?
1 Choice of variables.
 number of promotions 1 (P1)
number of promotions 1 (P1)
 number of promotions 2 (P2)
number of promotions 2 (P2)
2 Objective function
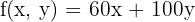
3 Constraints
| P1 | P2 | Available | |
| Tables | 1 | 3 | 400 |
| Chairs | 1 | 1 | 200 |
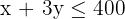
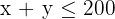


4 Find the feasible solution set
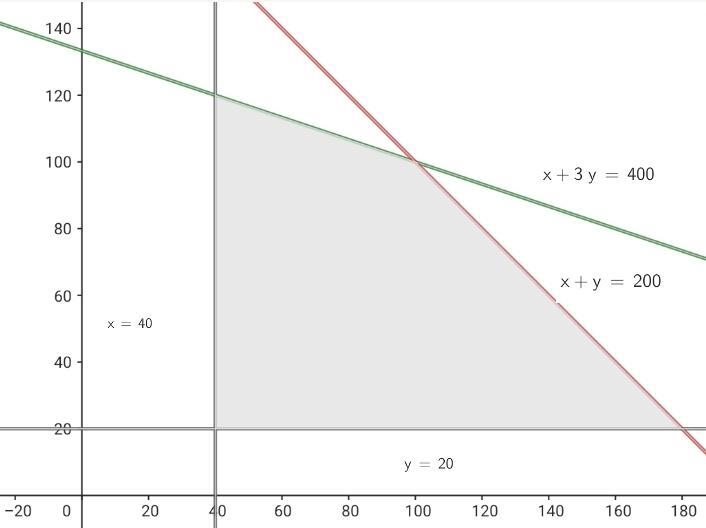
5 Calculate the coordinates of the vertices of the feasible solution region.
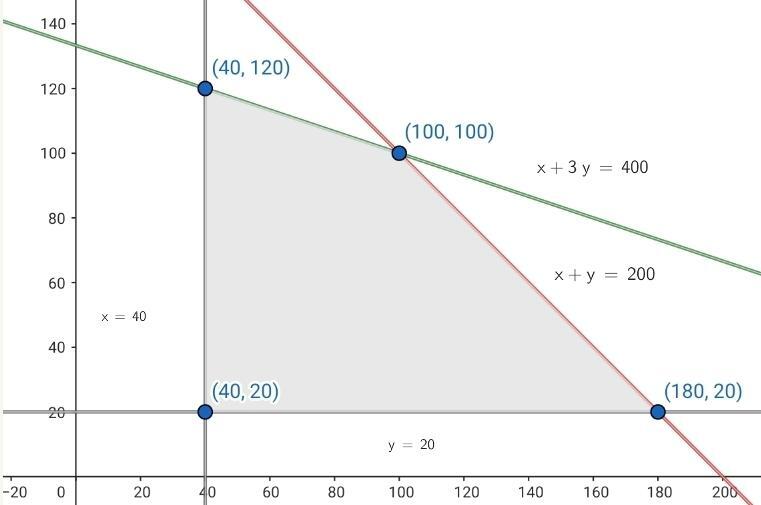
The vertices are: 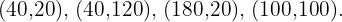
6 Calculate the value of the objective function


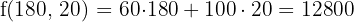
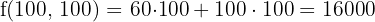 Maximum
Maximum
With 100 promotions of each type, the maximum profit of $16,000 is obtained.
Julian has a micro-business of pots and puts up for sale a cookware set in two presentations, an economical one and a luxury one. The material cost will be $20 for the economical one and $80 for the luxury one. The labor cost is $50 for the economical one and $80 for the luxury one. Julian has $160,000 available for materials and $240,000 for staff payment. If the economical set sells for $100 and the luxury one for $230, what production model should Julian follow for maximum sales?
1 Choice of variables.
 number of economical sets
number of economical sets
 number of luxury sets
number of luxury sets
2 Objective function

3 Constraints
| Economical | Luxury | Available | |
| Material | 20 | 80 | 160,000 |
| Labor | 50 | 80 | 240,000 |
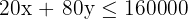
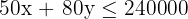


4 Find the feasible solution set
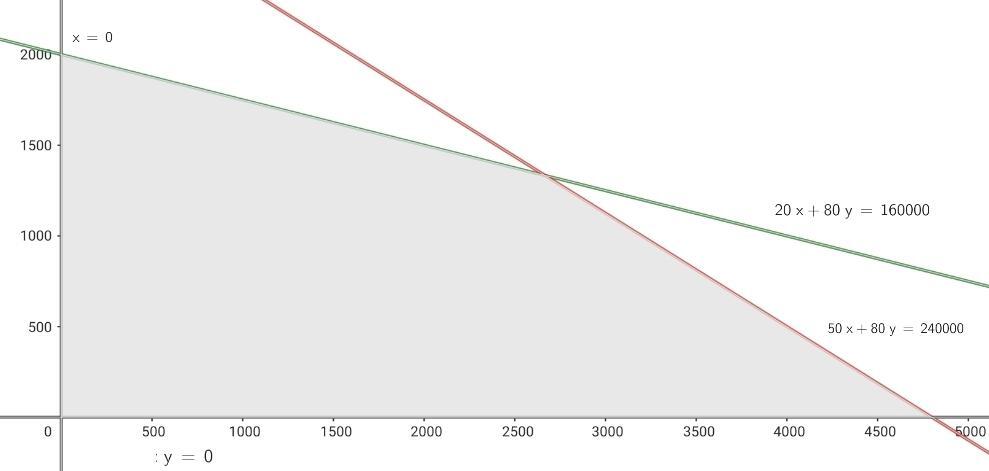
5 Calculate the coordinates of the vertices of the feasible solution region.
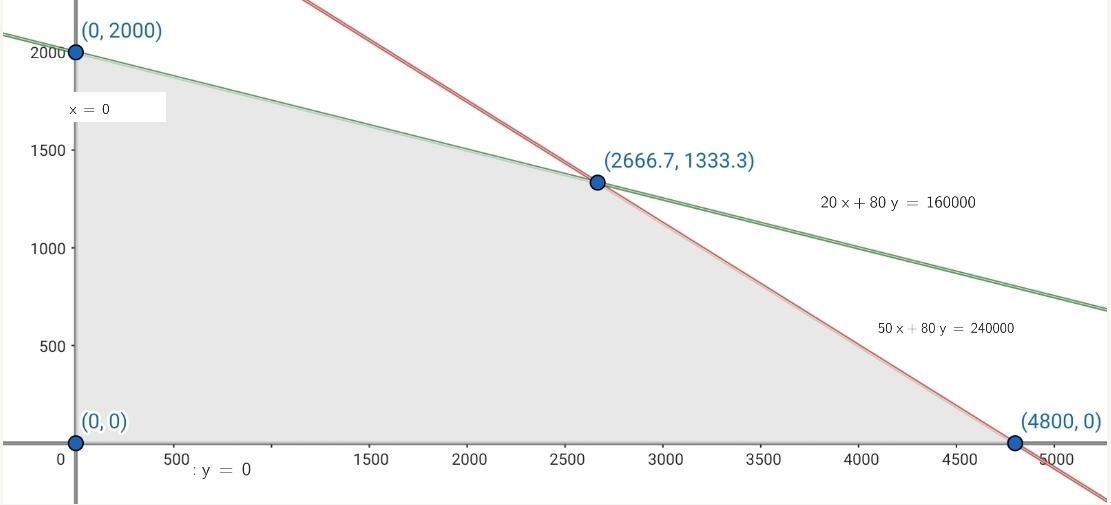
The vertices are: 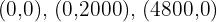 and the vertex
and the vertex 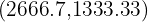 which can be rounded to the vertex
which can be rounded to the vertex 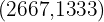 since quantities can only be positive integers.
since quantities can only be positive integers.
6 Calculate the value of the objective function
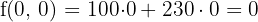
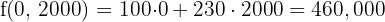
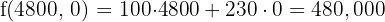
 Maximum
Maximum
With the production and sale of 2667 economical sets and 1333 luxury sets, Julian will obtain the maximum sales of $573,290.
A farmer has 600 acres where he can plant corn or barley and has 800 hours of work available during the season. The profit margins per hectare for corn are $60 and for barley is $70. The labor requirements to work in corn planting is 1 hour per acre and in barley planting is 2 hours per acre. How many acres of each crop should he plant to maximize his profit? What is the maximum profit?
1 Choice of variables.
 number of acres of corn
number of acres of corn
 number of acres of barley
number of acres of barley
2 Objective function

3 Constraints
| Corn | Barley | Available | |
| Acres | 1 | 1 | 600 |
| Hours | 1 | 2 | 800 |




4 Find the feasible solution set
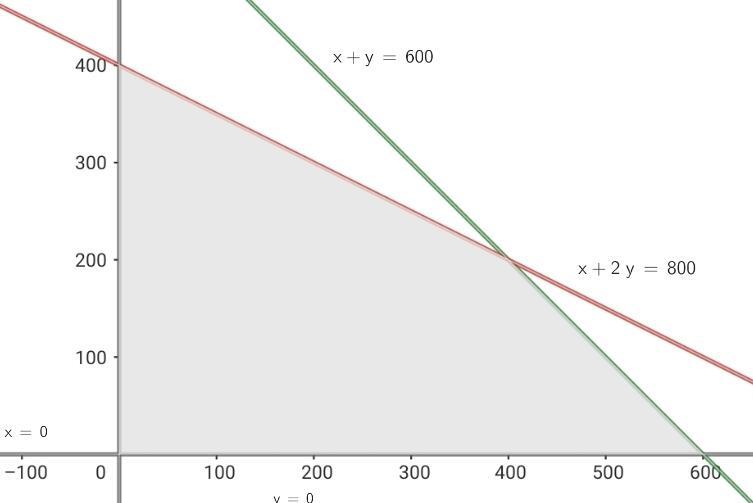
5 Calculate the coordinates of the vertices of the feasible solution region.
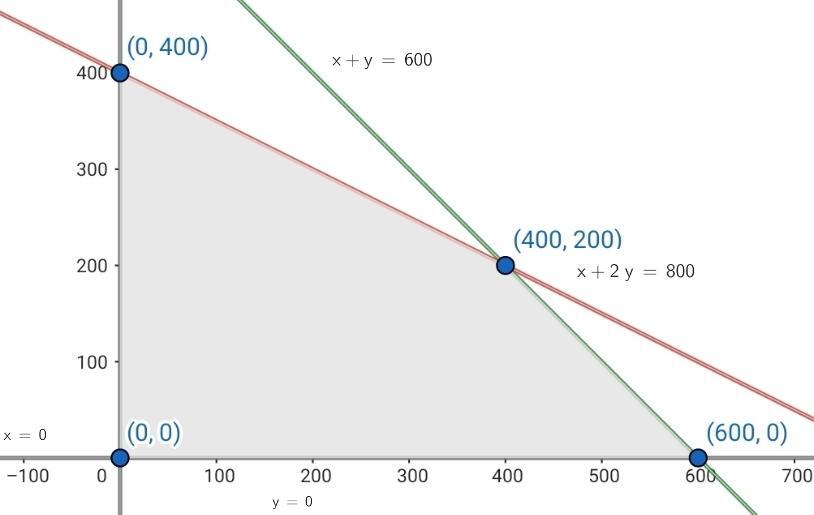
The vertices are: 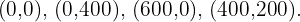
6 Calculate the value of the objective function
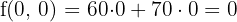
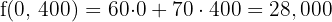

 Maximum
Maximum
The farmer should plant 400 acres of corn and 200 of barley to obtain the maximum profit of $38,000.
A company decides, for Workers' Day, to take 400 workers (at least) on a trip to the beach. To do this, they hire a transportation company, which has buses for 60 passengers and minibuses for 20 passengers. The rental price for each bus is $250 and for each minibus $200. The transportation company only has 8 professional drivers available that day. What number of buses and minibuses should be hired for minimum cost?
1 Choice of variables.
 number of buses
number of buses
 number of minibuses
number of minibuses
2 Objective function

3 Constraints
| Buses | Minibuses | Available | |
| Passengers | 60 | 20 | 400 |
| Drivers | 1 | 1 | 8 |
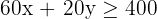
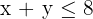


The first inequality is because at least 400 employees will go, but we can devise a transportation plan where there are available seats as long as the cost is minimum.
4 Find the feasible solution set
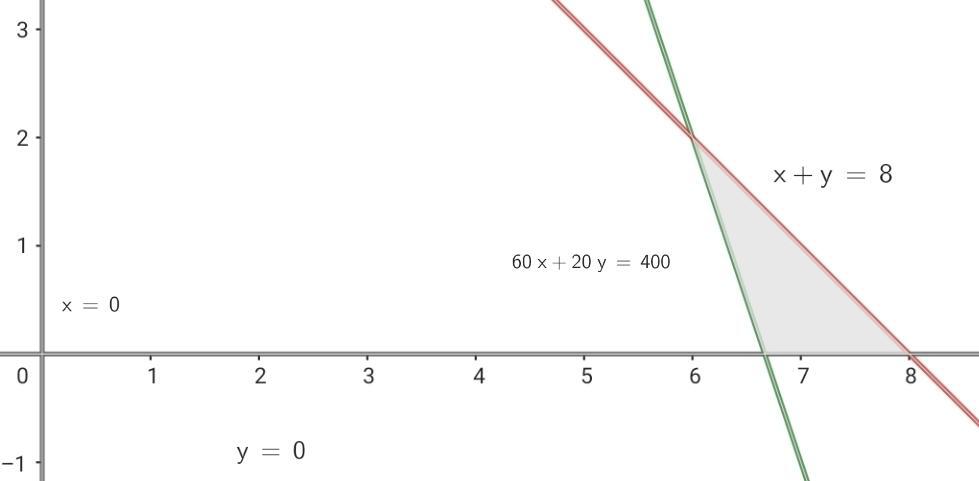
5 Calculate the coordinates of the vertices of the feasible solution region.
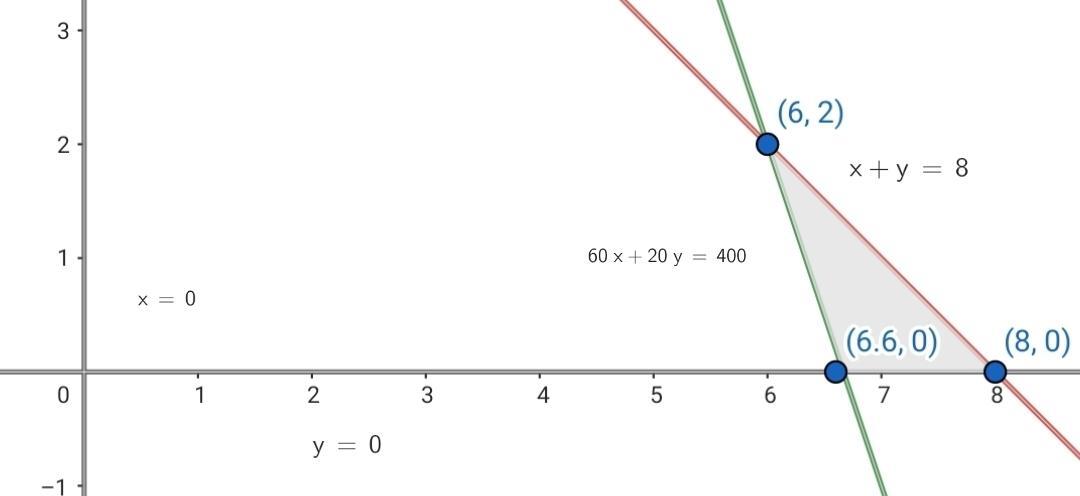
The vertices are: 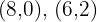 and the vertex
and the vertex 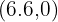 which can be rounded to the vertex
which can be rounded to the vertex 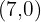 since quantities can only be positive integers.
since quantities can only be positive integers.
6 Calculate the value of the objective function
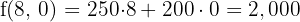
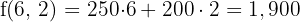
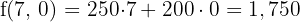 Minimum
Minimum
Therefore, with 7 buses with capacity for 420 passengers, the company will spend the minimum of $1,750.
If you're thinking you need math classes, don't hesitate to check out Superprof, where you'll find the best professionals, whether you're looking for an online math teacher or an in-person one.
Summarize with AI:


