Chapters

Elimination (or Reduction) Method
The elimination method consists of adding or subtracting  equations to obtain a third one. This new equation will have one fewer variable than the original equations, making it possible to solve for one of the variables.
equations to obtain a third one. This new equation will have one fewer variable than the original equations, making it possible to solve for one of the variables.
Example
Given the following system of equations:
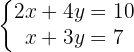
Notice that this is a system of two equations with two unknowns, so we can assume the system has a unique solution. Then:
Step 1: Check whether the two equations can be added or subtracted in such a way that one of the variables is eliminated.
If it is not possible to eliminate a variable directly, we must multiply one or both equations by some value so that one of the variables has the same coefficient in both equations.
Step 2: Once the variables have the same coefficient, we subtract the equations to eliminate one of the variables.
Step 3: In the resulting equation, we solve for the remaining variable.
Step 4: Substitute that value into one of the original equations to find the value of the other variable.
Let’s solve:

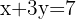
Step 1: Since none of the variables have the same coefficient, we need to multiply one equation. We multiply the second equation by  :
:

Now we have:

Step 2: Since we now have equal coefficients for one of the variables, we can subtract the equations:

Step 3: Solve for  .
.
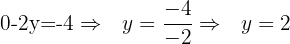
Step 4: Substitute  into either the first or the second equation.
into either the first or the second equation.

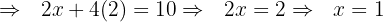
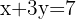

Let's work on some exercises!
Solve the system – Integer coefficients
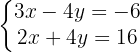
Since both equations have the same coefficient for the variable  , but with opposite signs, we add the two equations.
, but with opposite signs, we add the two equations.
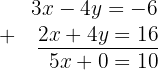
We solve for the variable to find its value:
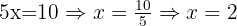
We substitute the value of  into the second original equation.
into the second original equation.
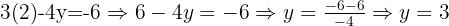
The solution is:
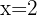 and
and 
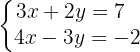
We eliminate the  variable. To do this, we multiply the first equation by
variable. To do this, we multiply the first equation by  and the second equation by
and the second equation by  .
.
We add both equations term by term and obtain the value of  .
.
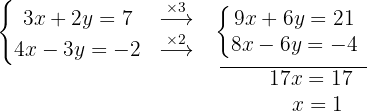
We substitute the value of  into the first original equation.
into the first original equation.
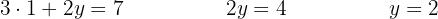
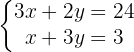
We eliminate the  variable. To do this, we multiply the second equation by
variable. To do this, we multiply the second equation by  .
.
We add both equations term by term and obtain the value of  .
.
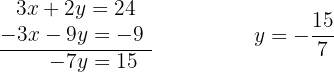
We substitute the value of  into the second original equation.
into the second original equation.
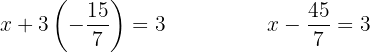
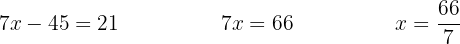
Solve the system – Rational coefficients
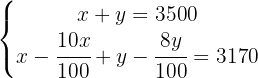
We remove denominators in the second equation by multiplying  by
by 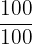 .
.
This fraction is equal to  , so it does not change the proportionality of the equation. It is simply a trick to make the calculation easier.
, so it does not change the proportionality of the equation. It is simply a trick to make the calculation easier.
We obtain:
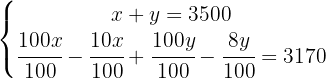
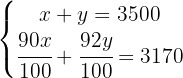
To eliminate the denominators in the second equation, we multiply  by
by  .
.
The new system obtained is:
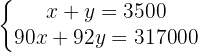
We are going to use the elimination method. To do this, we need to eliminate one of the two unknowns when adding the equations. We can multiply the first equation by  in order to eliminate
in order to eliminate  .
.
By adding the two equations, we obtain an equation with only one unknown (the variable  ).
).
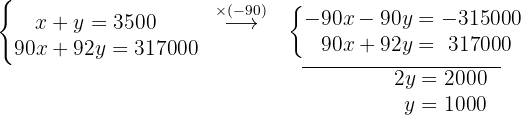
We obtain the value of  :
:

We substitute the value of  into the first original equation.
into the first original equation.

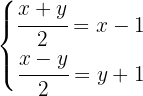
We remove denominators. To do this, we multiply both equations by  , since this is the only denominator that appears in both.
, since this is the only denominator that appears in both.
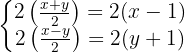
Since on the left-hand side of the equations we are multiplying and dividing by the same number, the  cancels out.
cancels out.
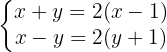
We remove parentheses:
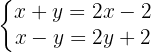
We rearrange the terms, placing the variables on one side and the constant term on the other:
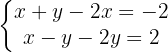
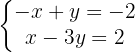
Since the equations contain  and
and  , we can now apply elimination directly (by adding the equations), because the variable
, we can now apply elimination directly (by adding the equations), because the variable  will be eliminated, as
will be eliminated, as 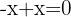 .
.
We add both equations term by term and calculate the value of  .
.
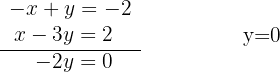
We substitute the value of  into the second equation of the system (you may also use the first one) and solve.
into the second equation of the system (you may also use the first one) and solve.
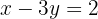

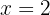
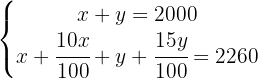
We remove the denominators from the second equation by multiplying by  , since it is the only denominator that appears.
, since it is the only denominator that appears.


We cancel the  in the terms where it appears multiplying and dividing, since .
in the terms where it appears multiplying and dividing, since .
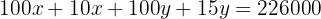
We add like terms to simplify.
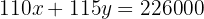
We are going to eliminate the variable  . To do this, we multiply the first equation by
. To do this, we multiply the first equation by 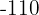 .
.
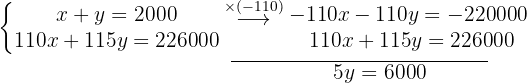
We obtain the value of  .
.
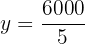

We substitute the value of  into the first equation and solve.
into the first equation and solve.


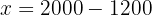
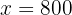
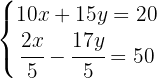
We begin by removing the denominators from the second equation. We do this by multiplying the second equation by  :
:
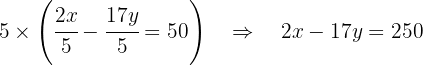
We now multiply this equation by  :
:
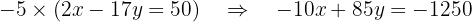
Now we add this equation to the first one in order to eliminate the variable  :
:
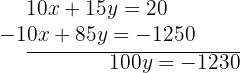
Therefore, we have:
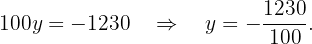
Thus,
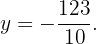
Now we substitute this value of  into either of the two equations to obtain the value of
into either of the two equations to obtain the value of  . For example, we substitute it into the first equation and simplify.
. For example, we substitute it into the first equation and simplify.

Thus, the solution of the system of equations is:
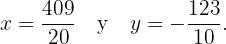
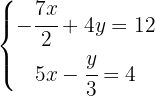
We begin by removing the denominators from the equations. We do this by multiplying the first equation by  and the second equation by
and the second equation by  :
:
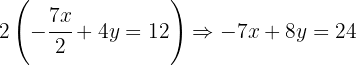
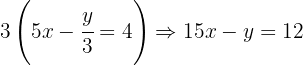
We now multiply the second equation by  :
:
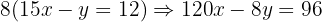
Now we add this equation to the first one to eliminate the variable  :
:
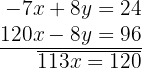
Therefore, we have:
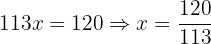
Now we substitute this value of  into either of the two equations to obtain the value of
into either of the two equations to obtain the value of  . For example, we substitute it into the first one and simplify.
. For example, we substitute it into the first one and simplify.

Thus, the solution of the system of equations is:
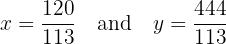
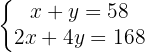
We are going to eliminate the variable  by multiplying the first equation by
by multiplying the first equation by  .
.
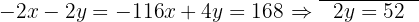
We calculate the value of  .
.
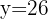
We substitute the value of  into the first equation.
into the first equation.

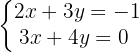
We are going to eliminate the variable  . To do this, we multiply the first equation by
. To do this, we multiply the first equation by  and the second equation by
and the second equation by  .
.
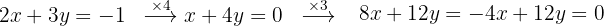
We subtract the first equation from the second in order to eliminate the variable  .
.
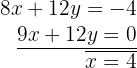
We obtain the value of the variable  .
.
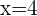
We substitute the value of  into one of the original equations.
into one of the original equations.
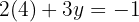
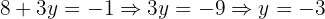
The solution is:
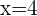 and
and 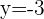
If you need more help, you can also find the perfect math tutor for you on Superprof.
Summarize with AI:












