Chapters

Fundamental Trigonometric Identities
1 Relationship between sine and cosine
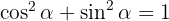
2 Relationship between secant and tangent
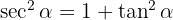
3 Relationship between cosecant and cotangent

4 Reciprocal trigonometric functions
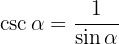
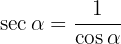

Examples of Exercises with Fundamental Trigonometric Identities
Knowing that 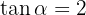 , and that 180° <
, and that 180° <  < 270°, calculate the remaining trigonometric ratios of angle
< 270°, calculate the remaining trigonometric ratios of angle 
Let's obtain the other trigonometric functions evaluated at this angle. We'll start with  since we can obtain it directly from
since we can obtain it directly from 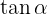
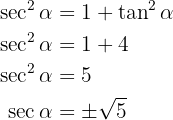
However, note that for the quadrant (or range) where  is defined, it holds that
is defined, it holds that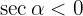 , therefore, we have
, therefore, we have 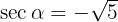
Now we can obtain 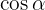
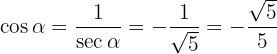
Let's obtain 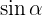 and from this
and from this 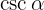 . Just like with
. Just like with 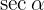 , sine is negative for the quadrant in which
, sine is negative for the quadrant in which  is defined, so
is defined, so
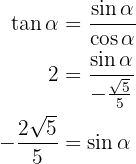
So we've obtained 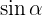 , now note that
, now note that
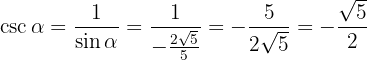
Finally, let's obtain 
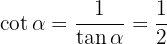
Knowing that 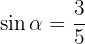 , and that 90° <
, and that 90° <  < 180°, calculate the remaining trigonometric ratios of angle
< 180°, calculate the remaining trigonometric ratios of angle 
Let's obtain the other trigonometric functions evaluated at this angle. We'll start with 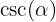 since we can obtain it directly
since we can obtain it directly

Now we can obtain 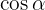 , note that for the interval where
, note that for the interval where  is defined, cosine is negative, so
is defined, cosine is negative, so
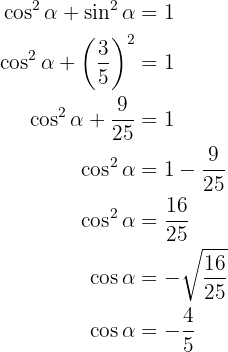
Since we have cosine, we can obtain 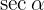 directly
directly

We only need to obtain tangent and cotangent, which we get from sine and cosine

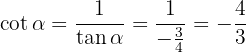
Trigonometric Ratios for Sum and Difference of Angles
1. 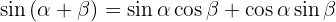
2. 
3. 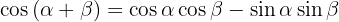
4. 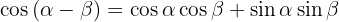
5. 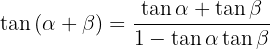
6. 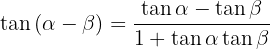
Examples of Exercises with Sum and Difference of Angles
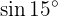
To solve this exercise, we will express our angle as the sum of two specific angles, in order to use the trigonometric function formulas applied to the sum and difference of angles.
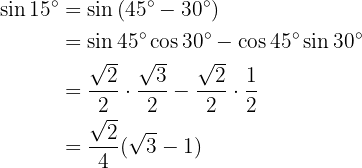

To solve this exercise, we will express our angle as the sum of two specific angles, in order to use the trigonometric function formulas applied to the sum and difference of angles.
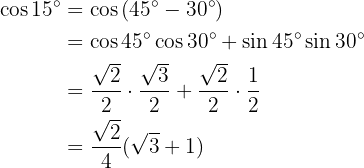
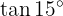
To solve this exercise, we will express our angle as the sum of two specific angles, in order to use the trigonometric function formulas applied to the sum and difference of angles.
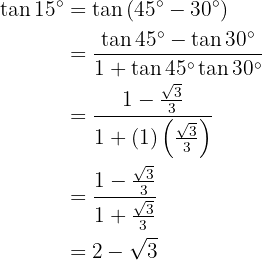
Trigonometric Ratios for Double Angles
1. 
2. 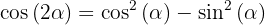
3. 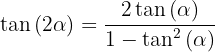
Examples of Exercises with Double Angles
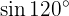
To solve this exercise, we will first find half of the given angle and then use the corresponding double-angle trigonometric function formula.
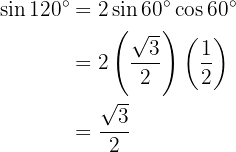
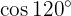
To solve this exercise, we will first find half of the given angle and then use the corresponding double-angle trigonometric function formula.
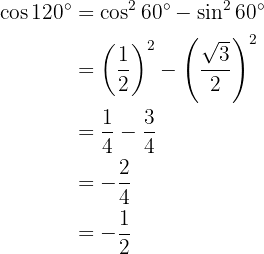
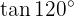
To solve this exercise, we will first find half of the given angle and then use the corresponding double-angle trigonometric function formula.
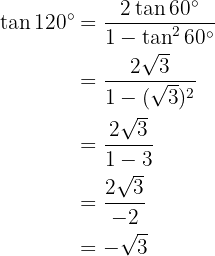
Trigonometric Ratios for Half Angles
1. 
2. 
3. 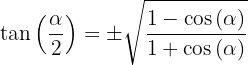
Examples of Half-Angle Exercises
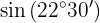
To solve this exercise, we will first find twice the given angle and then apply the formula corresponding to the given trigonometric function. Note that, due to the quadrant where the angle lies, the sine value will be positive.
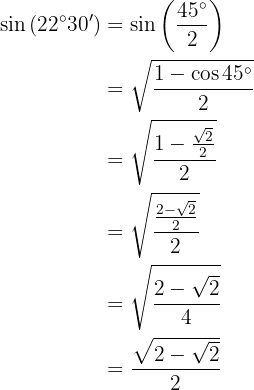

To solve this exercise, we will first find twice the given angle and then apply the formula corresponding to the given trigonometric function. Note that, due to the quadrant where the angle lies, the cosine value will be positive.
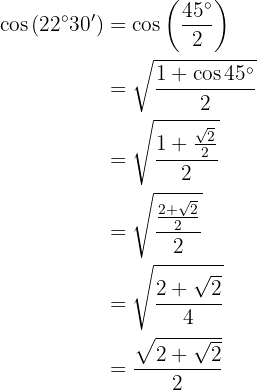
To solve this exercise, we will first find twice the given angle and then apply the formula corresponding to the given trigonometric function. Note that, due to the quadrant where the angle lies, the tangent value will be positive.
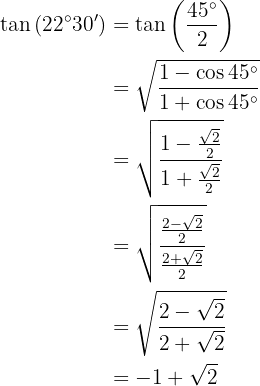
Transformation of Operations
Transformations of Sums into Products
1. 
2. 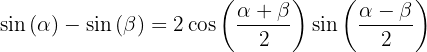
3. 
4. 
Examples of Transformations of Sums into Products
In the following exercises we will not write the value of the sum, or difference, of the sum of the trigonometric functions, we will simply transform it into a product of other trigonometric functions, according to the formula that should be applied.
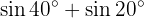
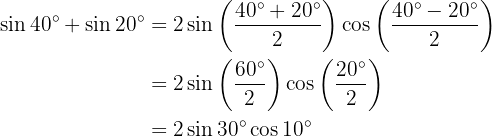
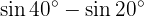
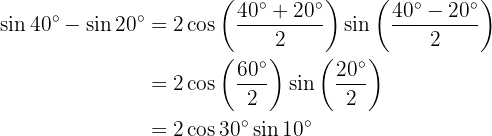
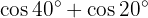
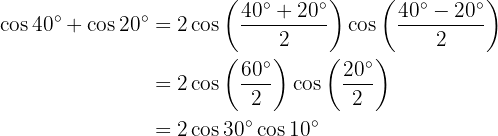
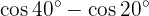
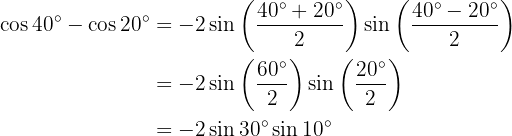
Transformations of Products into Sums
1. 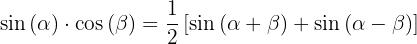
2. 
3. 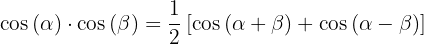
4. 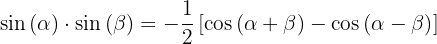
Examples of Transformations of Products into Sums
In the following exercises we will not write the value of the multiplication of the trigonometric functions, we will simply transform it into the sum, or difference, of other trigonometric functions, according to the formula that should be applied.
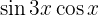

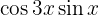
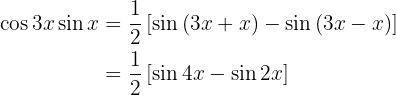
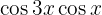
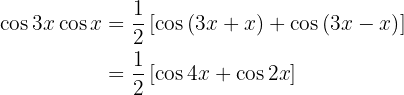

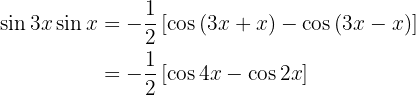
Summarize with AI:












