Welcome to the exercises on variance, mean deviation, and standard deviation! In this series of exercises, we will explore fundamental concepts in statistics that will help us understand the dispersion and variability of a data set.
Variance, mean deviation, and standard deviation are statistical measures that allow us to quantify the dispersion or variability of a data set with respect to its mean. These measures are especially useful for understanding how dispersed or grouped the values of a data set are and how they are distributed around their central value.
Get ready to strengthen your skills in statistics and discover the fascinating world of data analysis. Let's get started!
Find the mean deviation, the variance, and the standard deviation of  .
.
1 We compute the mean for the series of numbers 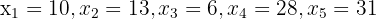 , with n=5=N. We have the following computations.
, with n=5=N. We have the following computations.
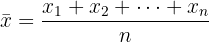
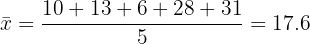
2 We compute the value of the mean deviation.
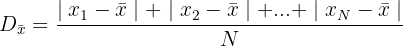

3 Now, we compute the value of the variance.
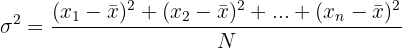
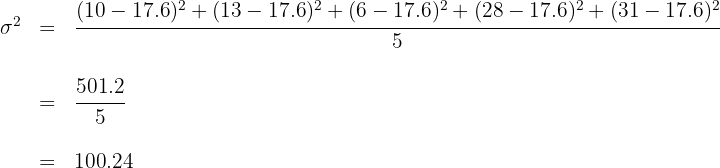
4 And finally, we compute the value of the standard deviation.

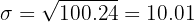
Find the mean deviation, the variance, and the standard deviation of the following series of numbers:
a 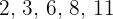 .
.
b 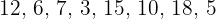 .
.
a For the series of numbers 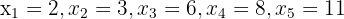 with we have the following calculations:
with we have the following calculations:
For the mean deviation, we first need to compute the mean.
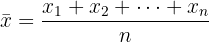

We compute the value of the mean deviation.
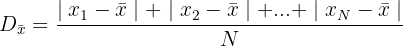

Now, we compute the value of the variance.
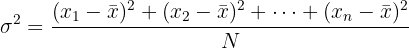
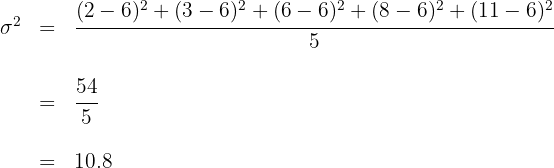
And finally, we compute the value of the standard deviation.


b For the series of numbers  with
with  , we have the following computations.
, we have the following computations.
For the mean deviation, we first need to compute the mean.
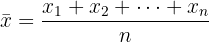

Then, we compute the value of the mean deviation.
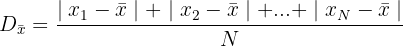
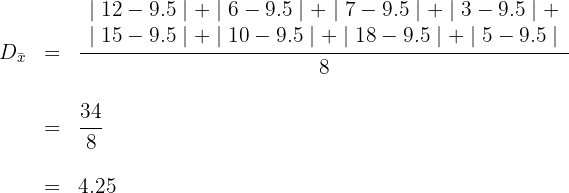
Now, we compute the value of the variance.
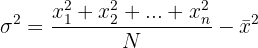

And finally, we compute the value of the standard deviation.
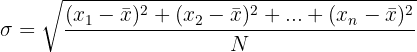

Find the variance and the standard deviation of 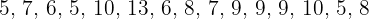 .
.
1 We build the frequency table and include the product of the variable by its absolute frequency  to compute the mean, and the product of the squared variable by its absolute frequency
to compute the mean, and the product of the squared variable by its absolute frequency 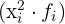 to compute the variance and the standard deviation.
to compute the variance and the standard deviation.
 |  |  |  |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 3 | 15 | 75 |
| 6 | 2 | 12 | 72 |
| 7 | 2 | 14 | 98 |
| 8 | 2 | 16 | 128 |
| 9 | 3 | 27 | 243 |
| 10 | 2 | 20 | 200 |
| 13 | 1 | 13 | 169 |
| 15 | 117 | 985 |
2 We compute the arithmetic mean.

3 We compute the variance.
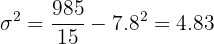
4 We compute the standard deviation.

A pediatrician obtained the following table about the age (in months) of 50 children from their practice at the time they walked for the first time. Compute the variance.
| Months | Children |
|---|---|
| 9 | 1 |
| 10 | 4 |
| 11 | 9 |
| 12 | 16 |
| 13 | 11 |
| 14 | 8 |
| 15 | 1 |
We complete the table with:
1 The product of the variable by its absolute frequency  to compute the mean.
to compute the mean.
2 The product of the squared variable by its absolute frequency 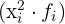 to compute the variance and the standard deviation.
to compute the variance and the standard deviation.
 |  |  |  |
|---|---|---|---|
| 9 | 1 | 9 | 81 |
| 10 | 4 | 40 | 400 |
| 11 | 9 | 99 | 1089 |
| 12 | 16 | 192 | 2304 |
| 13 | 11 | 143 | 1859 |
| 14 | 8 | 112 | 1568 |
| 15 | 1 | 15 | 225 |
| 50 | 610 | 7526 |
Review these concepts with our math tutor.
We compute the arithmetic mean.
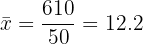
We compute the variance.
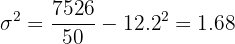
The result of rolling two dice 120 times is given by the table. Compute the variance.
| Sums | Times |
|---|---|
| 2 | 3 |
| 3 | 8 |
| 4 | 9 |
| 5 | 11 |
| 6 | 20 |
| 7 | 19 |
| 8 | 16 |
| 9 | 13 |
| 10 | 11 |
| 11 | 6 |
| 12 | 4 |
1 We add the columns 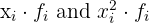
| x_i | f_i | x_i * f_i | x_i^2 * f_i |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 3 | 6 | 12 |
| 3 | 8 | 24 | 72 |
| 4 | 9 | 36 | 144 |
| 5 | 11 | 55 | 275 |
| 6 | 20 | 120 | 720 |
| 7 | 19 | 133 | 931 |
| 8 | 16 | 128 | 1024 |
| 9 | 13 | 117 | 1053 |
| 10 | 11 | 110 | 1100 |
| 11 | 6 | 66 | 726 |
| 12 | 4 | 48 | 576 |
| 120 | 843 | 6633 |
2 We compute the arithmetic mean.
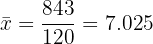
3 We compute the variance.
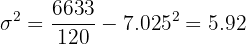
Compute the variance of a statistical distribution given by the following table.
 | |
|---|---|
| [10, 15) | 3 |
| [15, 20) | 5 |
| [20, 25) | 7 |
| [25, 30) | 4 |
| [30, 35) | 2 |
1 We add the columns 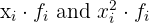
 |  |  |  | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10, 15) | 12.5 | 3 | 37.5 | 468.75 |
| [15, 20) | 17.5 | 5 | 87.5 | 1,531.25 |
| [20, 25) | 22.5 | 7 | 157.5 | 3,543.75 |
| [25, 30) | 27.5 | 4 | 110 | 3,025 |
| [30, 35) | 32.5 | 2 | 65 | 2,112.5 |
| 21 | 457.5 | 10,681.25 |
2 We compute the mean.

3 We compute the variance.

Compute the variance of the distribution in the table.
 |  |  |  | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [10, 20) | 15 | 1 | 15 | 225 |
| [20, 30) | 25 | 8 | 200 | 5,000 |
| [30, 40) | 35 | 10 | 350 | 12,250 |
| [40, 50) | 45 | 9 | 405 | 18,225 |
| [50, 60) | 55 | 8 | 440 | 24,200 |
| [60, 70) | 65 | 4 | 260 | 16,900 |
| [70, 80) | 75 | 2 | 150 | 11,250 |
| 42 | 1,820 | 88,050 |
1 We compute the mean.
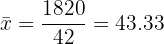
2 We compute the variance.

The heights of the players on a basketball team are given by the table. Compute the variance.
| Height | Number of Players |
|---|---|
| [5.6ft, 5.7ft) | 1 |
| [5.7ft, 5.9ft) | 3 |
| [5.9ft, 6.1ft) | 4 |
| [6.1ft, 6.2ft) | 8 |
| [6.2ft, 6.4ft) | 5 |
| [6.4ft, 6.6ft) | 2 |
1 We complete the table with the columns 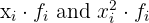
 |  |  |  |  | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [5.6ft, 5.7ft) | 5.7ft | 1 | 1 | 5.7ft | 9.8ft |
| [5.7ft, 5.9ft) | 5.8ft | 3 | 4 | 17.5ft | 31ft |
| [5.9ft, 6.1ft) | 6ft | 4 | 8 | 24ft | 43.7ft |
| [6.1ft, 6.2ft) | 6.2ft | 8 | 16 | 49.2ft | 92.3ft |
| [6.2ft, 6.4ft) | 6.3ft | 5 | 21 | 31.6ft | 60.8ft |
| [6.4ft, 6.6ft) | 6.5ft | 2 | 23 | 13ft | 25.6ft |
| 23 | 140.8ft | 263.2ft |
2 We compute the mean.
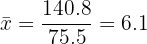
3 We compute the variance.
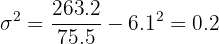
Given the statistical distribution, compute the variance.
 | |
|---|---|
| [0, 5) | 3 |
| [5, 10) | 5 |
| [10, 15) | 7 |
| [15, 20) | 8 |
| [20, 25) | 2 |
| [25, ∞) | 6 |
1 We complete the table with the columns 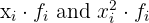
 |  |  | |
|---|---|---|---|
| [0, 5) | 2.5 | 3 | 3 |
| [5, 10) | 7.5 | 5 | 8 |
| [10, 15) | 12.5 | 7 | 15 |
| [15, 20) | 17.5 | 8 | 23 |
| [20, 25) | 22.5 | 2 | 25 |
[25,  ) ) | 6 | 31 | |
| 31 |
2 It is not possible to compute the mean, because it is not possible to find the class midpoint of the last interval.
3 If there is no mean, it is not possible to compute the variance.
Consider the following data:  . Then:
. Then:
a Compute its mean and its variance.
b If we multiply all the previous data by  , what will the new mean and variance be?
, what will the new mean and variance be?
We complete the table with the column 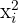
 | 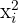 |
|---|---|
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 9 |
| 4 | 16 |
| 6 | 36 |
| 8 | 64 |
| 10 | 100 |
| 33 | 229 |
1 Mean and variance:
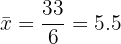
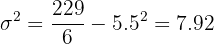
2 If all the values of the variable are multiplied by a number, the mean is multiplied by  and the variance is multiplied by the square of that number.
and the variance is multiplied by the square of that number.


Summarize with AI:


