Vector Addition
The operation of adding two or more vectors results in another vector. To perform vector addition there are different methods, either algebraically or using analytical geometry.
The algebraic method is known as the direct method.
The methods using analytical geometry are known as the polygon method which is used to add more than two vectors, the triangle method is the particular case of the polygon method when only two vectors are added, and the parallelogram method equally for adding two vectors.
Algebraic Method
1 Direct method
To add two or more vectors, their respective components of each vector are added.
In the case of two vectors, the addition is performed as follows:

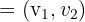

Example



Methods with Analytical Geometry
1 Triangle Method
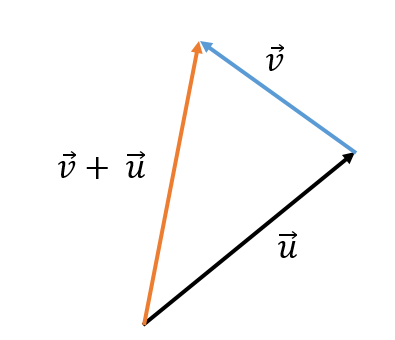
To add two free vectors  and
and  , two vectors are chosen as representatives such that the endpoint of one coincides with the origin of the other vector.
, two vectors are chosen as representatives such that the endpoint of one coincides with the origin of the other vector.
2 Parallelogram Method
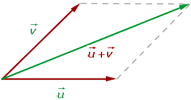
Two vectors with a common origin are taken as representatives, parallel lines are drawn to the vectors, obtaining a parallelogram whose diagonal coincides with the sum of the vectors.
3 Polygon Method
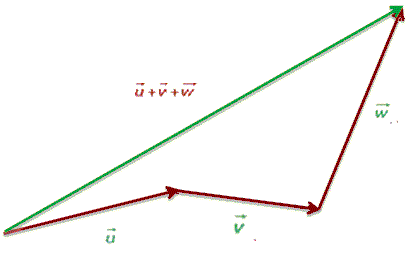
The polygon method is used when we want to add more than two vectors, and consists of placing one vector after another, so that the endpoint of one coincides with the origin of the other, and so on, until all vectors are placed. The resultant will be the vector that closes the polygon, that is, the one that goes from the beginning of the first to the endpoint of the last vector.
Vector Subtraction
The operation of subtracting two or more vectors results in another vector. To perform vector subtraction there are different methods, either algebraically or using analytical geometry.
The algebraic method is known as the direct method.
The methods using analytical geometry are known as the polygon method which is used to subtract more than two vectors, the triangle method is the particular case of the polygon method when only two vectors are subtracted, and the parallelogram method equally for subtracting two vectors.
Algebraic Method
1 Direct method
To subtract two free vectors  and
and  , we add
, we add  with the opposite of
with the opposite of  .
.
The components of the difference vector are obtained by subtracting the components of the vectors.

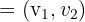

Example



Methods with Analytical Geometry
1 Triangle Method
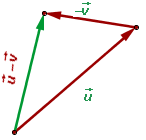
To subtract two free vectors  and
and  , we choose two vector representatives such that the endpoint of one coincides with the origin of the other vector.
, we choose two vector representatives such that the endpoint of one coincides with the origin of the other vector.
2 Parallelogram Method
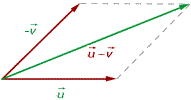
We take as representatives two vectors with a common origin, we draw parallel lines to the vectors obtaining a parallelogram whose diagonal coincides with the sum of the vectors.
3 Polygon Method
The polygon method is used when we want to subtract more than two vectors, and consists of placing one vector after another, so that the endpoint of one coincides with the origin of the other, and so on, until all vectors are placed. The resultant will be the vector that closes the polygon, that is, the one that goes from the beginning of the first to the endpoint of the last vector.
Properties of Vector Addition and Subtraction
1 Associative

2 Commutative

3 Identity Element

4 Opposite Element

Summarize with AI:












