A book musical is a type of musical theater with specific criteria – how many songs and how they are woven into the story; when the musical elements are introduced, and so on. Many people assume that a book musical is a stage show that includes music, whose inspiration is lifted from a previously published book. This is one of the ways a book musical can come to be, but it's not the only way. Discover what constitutes a book musical, find out how they are made, and learn about some of the most notable book musicals.

What Is a Book Musical?
Book musicals are just what they sound like: books (or stories) that are later adapted into musicals.
They tell a story, adapted for the stage through changing the dialogue and events as needed to adequately convey the tale through theater. The playwrights develop songs and lyrics, as well as a script, that tells the story they want to share based on the source material.
At times, the play is almost the same as the source. Other times, it's modified to tell a slightly different story.

The part that might confuse people is the reference to a book musical's book. This means the musical's libretto, which is the entirety of the work's script, including dance directions, lyrics and music, dialogue, and stage instructions, all together in one document.
Learn about concept musicals, which are very different from book musicals!
A book musical adapts a story from a previous work into a plot-based story for the stage. It incorporates important plot points and dialogue into songs.
Key Components of a Book Musical
Book musicals are just one genre of musical. They share the three main components of other musical works: libretto, musical score, and song lyrics. They are distinct from musicals like concept musicals in that they tell a story with character development, whereas concept musicals usually convey an artistic motif rather than a story.
The Book (Libretto)
The libretto is the entire script of a musical. It lays out:
- The narrative structure
- Character qualities, traits, motivations, and development
- Circumstances and situations that naturally allow the characters to break into song
Many theatrical branches use librettos: operas and operettas; cantatas and oratorios. Librettos even feature in religious practices such as requiems.
Check for online acting classes on Superprof.

Productions tend to run more smoothly from a libretto because they include stage directions. And, because the songs are integral to the story, it helps the performers get a sense of continuity when lyrics are included within the dialogue.
Musicals with strong books generally do well, even if their scores are not as strong as those of other musicals. Audiences want the musical to tell a cohesive story that makes them care about the characters. The only way to do that is to have a well-written script with all the musical lyrics, etc. built into the plot.
Libretto means "little book" in Italian. Since musicals are inspired by operas, it makes sense that the Italian terms were carried through.
The libretto helps the entire show understand the timeline, plot, motivations and feelings of the characters, and is required for the synergy needed in a good show.
Find out how film musicals brought this type of entertainment to the masses.
The Music
A score may include music played softly during characters’ conversational interludes as well as background music for action scenes, if any. It may even include orchestrations to be played during the intermission.
It is quite common for one person to write the music and another the lyrics; Gilbert and Sullivan were just such a writing team. The former wrote the libretti while the latter composed the music.
Across the pond, Rodgers and Hammerstein were an equally prolific creative team; Richard Rodgers composed the music, and Oscar Hammerstein wrote lines and lyrics.
musicals for Broadway, initiating the "golden age" of musical theater.
Find acting classes near me here on Superprof.
While collaborations are common in musical theater, some composers write their shows’ music and lyrics alone. An excellent, modern-day example of such is Lin-Manuel Miranda, author/composer of Hamilton.
In book musicals, many of the main themes are sung in the first act, with the second act's songs usually consisting mostly of reprieves. This conveys how the information learned in the first act is being resolved in the second.
These second-act tunes may be sung at a different tempo, by a chorus rather than the character who sang it first; they may even have different lyrics while the music remains the same. Occasionally, a new song and dance may be added.
Learn about the features of rock musicals.
The Lyrics
In some musicals, songs are meant as an aside to the audience, giving us a peek into the characters’ thoughts or motivations. By contrast, song lyrics in book musicals have a direct impact on the story itself.

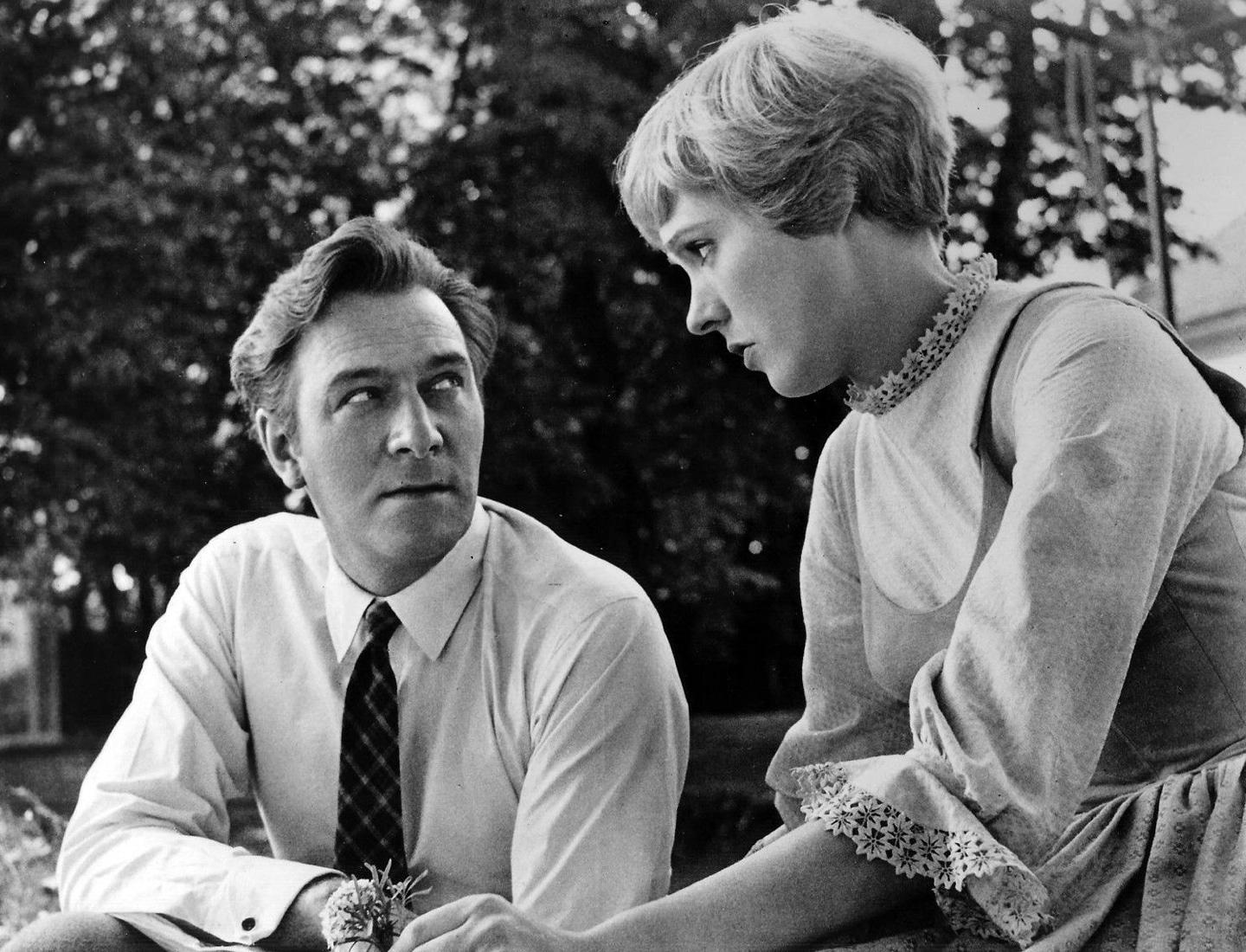
"Edelweiss," poignantly sung by the von Trapp family just before leaving Austria forever, is the perfect case in point.
Their audience includes Nazi officials, the very regime Captain von Trapp reviles, which he effectively demonstrates when he joins his son in singing about the pure, white flower that will forever symbolize his beloved Austria.
So effective was this ballad that many fans of "The Sound of Music" believed it was Austria’s national anthem (or at least a traditional folk song) when, in fact, it was written expressly for the play by American lyricist Oscar Hammerstein, who had no ties to Austria.
Learn to distinguish the characteristics of musical revues.
A score is the entirety of the music: the instrumentals and the lyrics (and singing).
Characteristics of Book Musicals
Book musicals are different from other types of musicals (such as concept musicals, jukebox musicals, and revue musicals) because of their structure and emphasis on storytelling through song and action.
However, many musicals fit more than one category; for example, "Rent" is both a book musical and a rock musical.
Find exceptional acting classes NYC on Superprof.
The most important feature of book musicals is the plot progression, just as you'd read in a book with a developed plot: there is a beginning, middle, and ending, with inciting incidents, rising action, a climax, and falling action.
Critically, the musical numbers in the play work to progress the plot.
Some musicals have musical numbers that don't change the situation very much by the time the song is over.
In those instances, it feels as if time stopped while the song was happening.

In book musicals, important dialogues and actions occur within the song.
Characters develop, change, and grow through the story.
In summary, watching a book musical feels like reading a well-written novel, but with music and dance included at crucial points.
Discover the key characteristics of other types of musicals.
When the emotion becomes too strong for speech, you sing; when it becomes too strong for song, you dance.
Ben Wattenberg, American author
The Most Popular Book Musicals
Book musicals generally appeal to the widest audience range. This is because they are very similar to media like Disney movies, which have compelling stories and characters, paired with memorable songs.
There have been many popular musicals over the years because of the genre's appeal. Some titles have remained iconic through time, while others are becoming modern-day classics.
Among the most popular examples of book musicals are:
| Musical | Book Based On | Musical Book (Libretto) Author | Score Author |
|---|---|---|---|
| Guys and Dolls | Short stories by Damon Runyon (mostly "The Idyll of Miss Sarah Brown" and "Blood Pressure") | Jo Swerling and Abe Burrows | Frank Loesser |
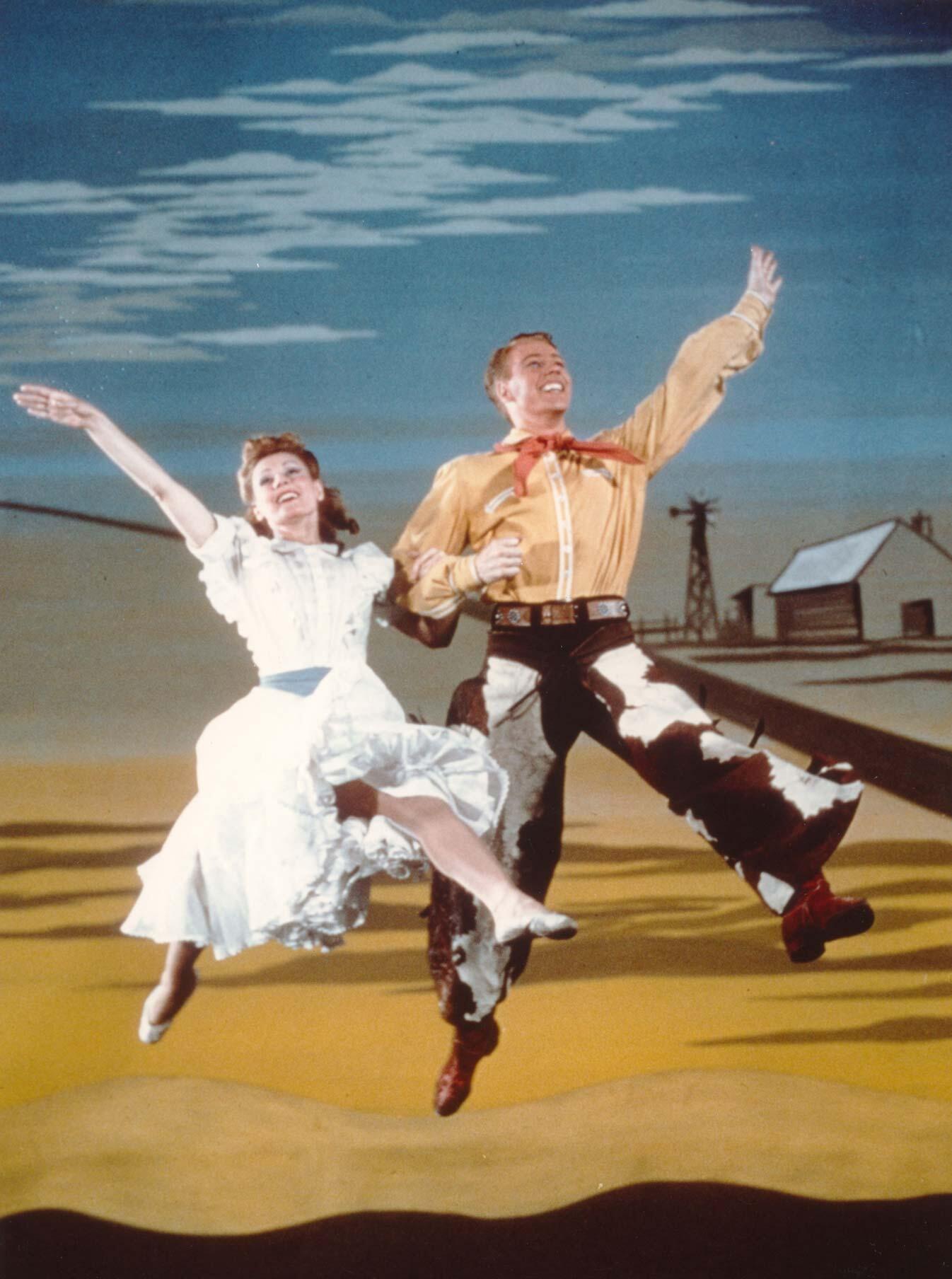
| Oklahoma! | "Green Grow the Lilacs" by Lynn Riggs (play) | Oscar Hammerstein | Richard Rodgers |
| Fiddler on the Roof | Short stories by Sholem Aleichem (mostly "Tevye and his Daughters" aka "Tevye the Dairyman") | Joseph Stein | lyrics by Sheldon Harnick, music by Jerry Bock |
| West Side Story | "Romeo & Juliet" by William Shakespeare (play) | Arthur Laurents | music by Leonard Bernstein, lyrics by Stephen Sondheim |
| Show Boat | "Show Boat" by Edna Ferber (novel) | Oscar Hammerstein | Jerome Kern |
| My Fair Lady | "Pygmalion" by George Bernard Shaw (play) | Alan Jay Lerner | Frederick Loewe |
| The King and I | "Anna and the King of Siam" by Margaret Landon (novel) | Oscar Hammerstein | Richard Rodgers |
| The Sound of Music | "The Story of the Trapp Family Singers" by Maria von Trapp (book) | Howard Lindsay and Russel Crouse | music by Richard Rodgers, lyrics by Oscar Hammerstein II |
| Les Misérables | "Les Misérables" by Victor Hugo (book) | Boublil and Schönberg | music by Claude-Michel Schönberg, lyrics by Alain Boublil and Jean-Marc Natel |
| Mary Poppins | the "Mary Poppins" children's book series by P. L. Travers & the 1964 Disney film | Julian Fellowes | Richard M. Sherman, Robert B. Sherman, George Stiles, Anthony Drewe |
| Evita | "The Woman with the Whip" by Mary Main (biography) | Tim Rice | music by Andrew Lloyd Webber, lyrics by Tim Rice |
| Charlie and the Chocolate Factory | "Charlie and the Chocolate Factory" by Roald Dahl (book) | David Greig | music by Marc Shaiman, lyrics by Shaiman and Scott Wittman |
| The Phantom of the Opera | "The Phantom of the Opera" by Gaston Leroux (book) | Lloyd Webber and Stilgoe | music by Andrew Lloyd Webber, lyrics by Charles Hart, additional lyrics by Richard Stilgoe |
| Rent | "La bohème" by Giacomo Puccini, Luigi Illica, and Giuseppe Giacosa (opera) | Jonathan Larson | Jonathan Larson |
| Wicked (Wicked: The Untold Story of the Witches of Oz) | "Wicked: The Life and Times of the Wicked Witch of the West" by Gregory Maguire (novel) | Winnie Holzman | Stephen Schwartz |
| Hamilton: An American Musical | "Alexander Hamilton" by Ron Chernow (biography) | Lin-Manuel Miranda | Lin-Manuel Miranda |
Now that you know more about book musicals, you can better determine which exciting shows you want to see on stage!
Also discover other types of musicals, like jukebox musicals, which have their own genre expectations and charm. Knowing the differences between different types of musicals means you can better appreciate the unique elements of each type.
🎵 What's your favorite book musical?
Summarize with AI:















