Chapters
Before jumping into the exercises, let's review the basics.

What Is a Quadratic Function?
A quadratic function is a second-degree polynomial function with the form: 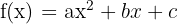 , where
, where  ,
,  , and
, and  are real constants, and
are real constants, and 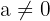 .
.
The graph of a quadratic function is one of the conic sections (circle, ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola), but in this section, we’ll focus only on parabolas.
The graph of 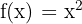 — the simplest quadratic function — reveals several key features of a parabola. For instance,
— the simplest quadratic function — reveals several key features of a parabola. For instance,  , and
, and 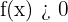 for any other real value of
for any other real value of  . This means the function has a minimum at the point
. This means the function has a minimum at the point 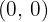 , which is called the vertex of the parabola.
, which is called the vertex of the parabola.
- If
 , the parabola opens upward (the vertex is at the bottom).
, the parabola opens upward (the vertex is at the bottom). - If
 , the parabola opens downward (the vertex is at the top).
, the parabola opens downward (the vertex is at the top).
How Do You Solve and Graph a Quadratic Function?
There are two main methods to solve and graph a quadratic function. Below are the steps for each:
✅ Vertex Formula Method
- 1 - Identify the values of
 ,
,  , and
, and  .
. - 2 - Find the
 -value of the vertex using the vertex formula.
-value of the vertex using the vertex formula. - 3 - Find the
 -value by plugging
-value by plugging  into the function.
into the function. - 4 - Write the vertex coordinates as
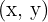 .
.
✅ Completing the Square Method
- 1 - Write out the equation.
- 2 - Divide all terms by the coefficient of
 .
. - 3 - Move the constant term to the right-hand side.
- 4 - Complete the square on the left-hand side.
- 5 - Factor the left-hand side.
- 6 - Solve and write the vertex coordinates
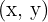 .
.
Proposed Exercises
Solve and Graph the Following Quadratic Functions
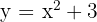
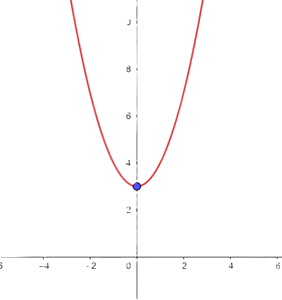
1 Vertex
We apply the vertex formula:
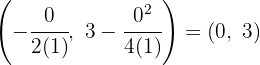
So, the vertex is 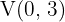 .
.
2 X-axis intercepts
We set the function equal to zero and calculate the solutions:
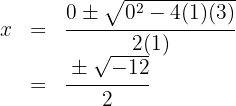
Which has no real solutions.
So, there are no intersections with the  axis.
axis.
3 Y-axis intercept
So, the intersection with the  axis is
axis is 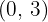 .
.
4 With the above information, the graphical representation is:
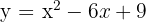
1 Vertex
We apply the vertex formula:
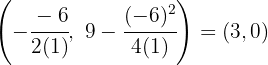
So, the vertex is 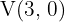 .
.
2 X-axis intercepts
We set the function equal to zero and calculate the solutions:
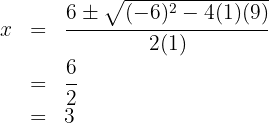
So, the intersections with the  axis are
axis are 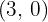 .
.
3 Y-axis intercept
So, the intersection with the  axis is
axis is 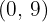 .
.
4 With the above information, the graphical representation is:
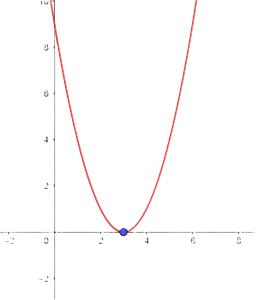

1 Vertex
We apply the vertex formula:
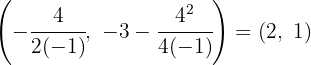
So, the vertex is 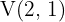 .
.
2 X-axis intercepts
We set the function equal to zero and calculate the solutions:
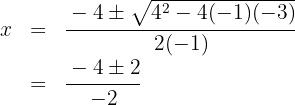
We get the solutions 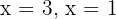
So, the intersections with the  axis are
axis are 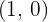 and
and 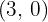 .
.
3 Y-axis intercept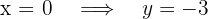
So, the intersection with the  axis is
axis is 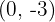 .
.
4 With the above information, the graphical representation is:
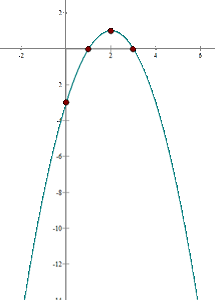
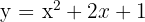
1 Vertex
We apply the vertex formula:
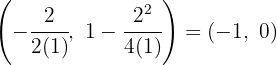
So, the vertex is 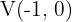 .
.
2 X-axis intercepts
We set the function equal to zero and calculate the solutions:
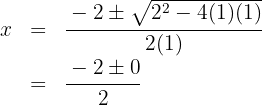
We get the solution 
So, the intersection with the  axis is
axis is 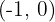 .
.
3 Y-axis intercept
So, the intersection with the  axis is
axis is 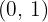 .
.
4 With the above information, the graphical representation is:
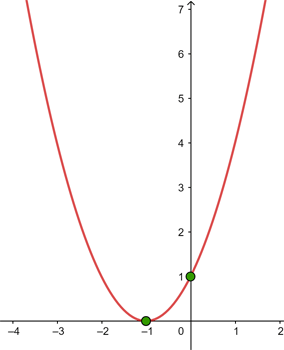

1 Vertex
We apply the vertex formula:
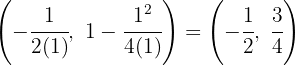
So, the vertex is 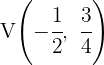 .
.
2 X-axis intercepts
We set the function equal to zero and calculate the solutions:
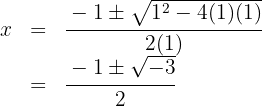
Since the discriminant is negative,  , there are no intersections with the
, there are no intersections with the  axis.
axis.
3 Y-axis intercept
So, the intersection with the  axis is
axis is 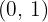 .
.
4 With the above information, the graphical representation is:
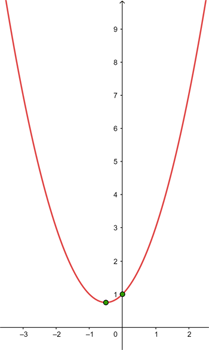
Find the vertex and the equation of the axis of symmetry for the following parabolas
1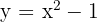 ;
;
2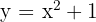 ;
;
3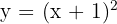 ;
;
4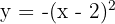 ;
;
5 ;
;
6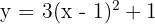 ;
;
7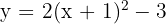 ;
;
8 ;
;
9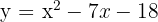 ;
;
10
The vertex of the parabola  is given by
is given by 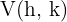 , and the axis of symmetry is
, and the axis of symmetry is  . For the parabola
. For the parabola 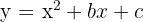 , the vertex is given by
, the vertex is given by 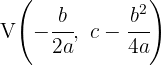
1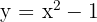
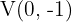

2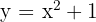
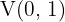

3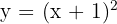
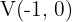

4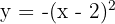
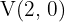

5
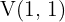

6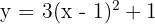
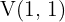

7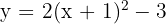


8


9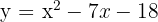
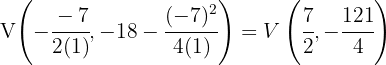
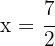
10
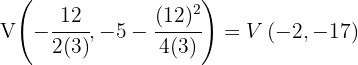

Without graphing, indicate how many times the following parabolas intersect the x-axis
1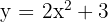 ;
;
2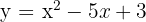 ;
;
3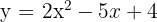 ;
;
4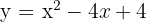 ;
;
5 .
.
We apply the discriminant  , and based on its sign, determine whether the parabolas intersect the x-axis twice, once, or not at all.
, and based on its sign, determine whether the parabolas intersect the x-axis twice, once, or not at all.
1. 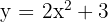
We calculate the discriminant:
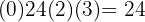
We calculate the discriminant:
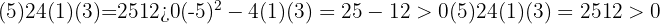
Since the discriminant is positive, there are two points of intersection.
3. 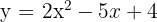
We calculate the discriminant:
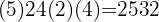
We calculate the discriminant:
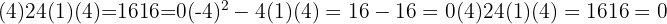
Since the discriminant is zero, there is one point of intersection.
5. 
We calculate the discriminant:
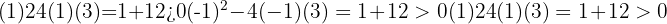
Since the discriminant is positive, there are two points of intersection.
A quadratic function has the form 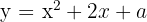 and passes through the point
and passes through the point 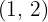 . Find the value of
. Find the value of  .
.
1 We substitute the point into the function
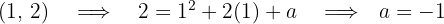
A quadratic function has the form  and passes through the point
and passes through the point 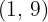 . Find the value of
. Find the value of  .
.
1 We substitute the point into the function: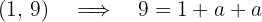
2 We solve for  :
: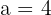
A quadratic function has the form  and passes through the points
and passes through the points 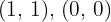 , and
, and 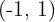 . Find
. Find 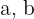 , and
, and  .
.
1 We substitute each point into  :
: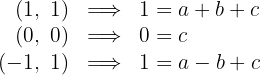
2 We obtain the following system of equations: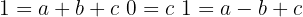
3 Solving the system, we get 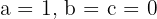
A parabola has its vertex at the point 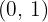 and passes through the point
and passes through the point 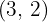 . Find its equation.
. Find its equation.
1 The equation is written in the form 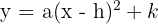
2 We substitute the values of the vertex: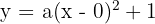
3 We substitute the point 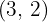 and solve for
and solve for  :
: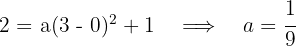
4 We substitute the value of  :
: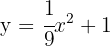
A parabola has its vertex at the point 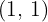 and passes through the point
and passes through the point 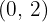 . Find its equation.
. Find its equation.
1 The equation is written in the form 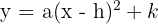
2 We substitute the values of the vertex:
3 We substitute the point 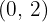 and solve for
and solve for  :
: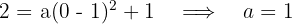
4 We substitute the value of  and expand:
and expand: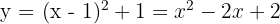
Starting from the graph of the function 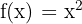 , represent:
, represent:
1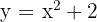 ;
;
2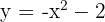 ;
;
3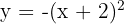 ;
;
4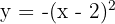 ;
;
5 ;
;
6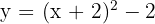 ;
;
7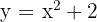 ;
;
8 ;
;
9 ;
;
10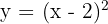 ;
;
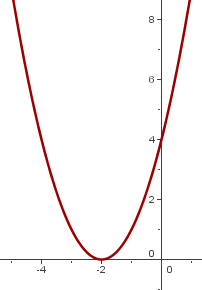
We will use the graph of 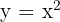 .
.
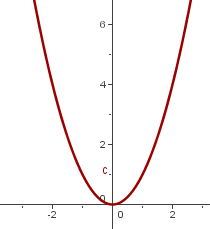
1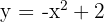
We reflect it over the x-axis and shift the graph of 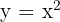 so the vertex is at
so the vertex is at 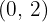
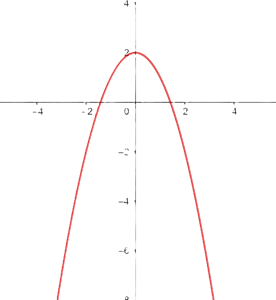
2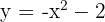
We reflect it over the x-axis and shift the graph of 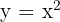 so the vertex is at
so the vertex is at 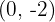
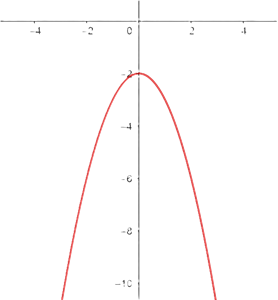
3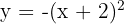
We reflect it over the x-axis and shift the graph of 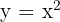 so the vertex is at
so the vertex is at 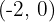
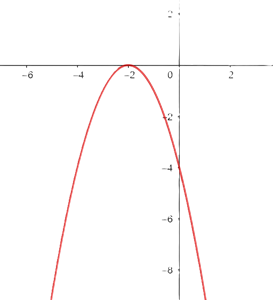
4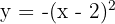
We reflect it over the x-axis and shift the graph of 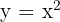 so the vertex is at
so the vertex is at 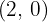
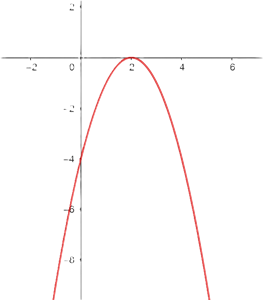
5
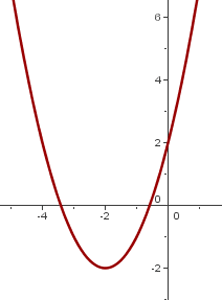
We shift the graph of 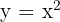 so the vertex is at
so the vertex is at 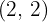
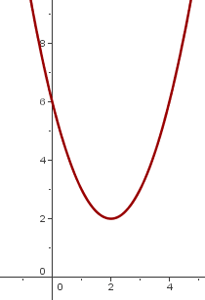
6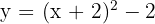
We shift the graph of 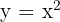 so the vertex is at
so the vertex is at 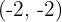
7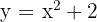
We shift the graph of 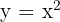 so the vertex is at
so the vertex is at 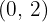
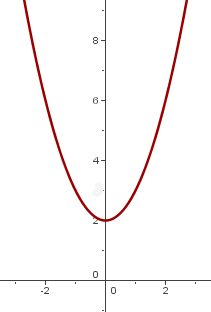
8
We shift the graph of 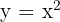 so the vertex is at
so the vertex is at 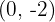
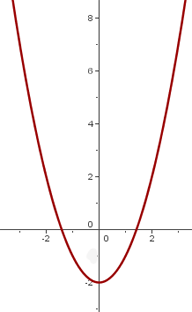
9
We shift the graph of 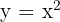 so the vertex is at
so the vertex is at 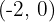
10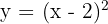
We shift the graph of 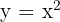 so the vertex is at
so the vertex is at 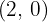
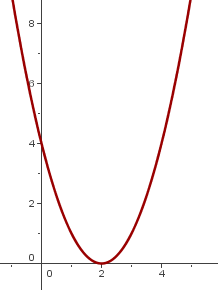
Find the equation of the parabola with focus 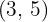 and vertex
and vertex 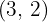 .
.
1 The focus is above the vertex, so the parabola opens upward.
2 We calculate the distance from the focus to the vertex, which is 3.
3 We use the formula: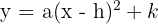
Where  equals the reciprocal of four times the distance from the focus to the vertex. So,
equals the reciprocal of four times the distance from the focus to the vertex. So, 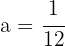
4 Then, the equation of the parabola is: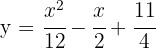
Find the equation of the parabola with focus 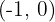 and vertex
and vertex 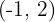 .
.
1 The focus is below the vertex, so the parabola opens downward.
2 We calculate the distance from the focus to the vertex, which is 2.
3 We use the formula: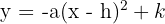
Where  equals the reciprocal of four times the distance from the focus to the vertex. So,
equals the reciprocal of four times the distance from the focus to the vertex. So, 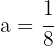
4 Then, the equation of the parabola is: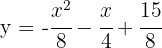
Summarize with AI:












