Welcome to our page dedicated to maxima and minima exercises! In this space, we will explore the exciting field of mathematical optimization and provide you with the knowledge and strategies necessary to solve problems involving finding the maximum and minimum values of functions.
Maxima and minima problems are found in various areas, such as physics, economics, engineering, and many others. These challenges invite us to find the critical points of a function, where the slope is zero, and determine whether those points correspond to local maxima or minima.
Here, you will learn to identify the key characteristics of a function that will allow you to determine its maxima and minima. We will do this by presenting you with a wide variety of exercises, which we will solve using the second derivative test.
Our goal is to help you develop your ability to find optimal solutions, strengthen your analytical reasoning, and promote your confidence in mathematics. Enjoy and learn with the various exercises, along with the clear and detailed explanations we have created for you. Become an expert at calculating maxima and minima of functions!
Use the second derivative test to calculate the local maxima and minima of the following functions:
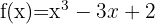
We begin by finding the first and second derivatives of the given function:
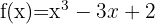
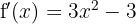
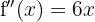
Now let's find the critical points  by solving the equation
by solving the equation  , that is
, that is 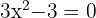 . The solutions to this equation are
. The solutions to this equation are 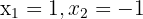 .
.
Finally, we evaluate  at the critical points
at the critical points  and determine whether
and determine whether 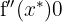 or
or 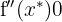 .
.
We have:
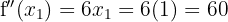
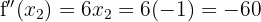
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has a local minimum at
has a local minimum at  and a local maximum at
and a local maximum at  . The corresponding function values are:
. The corresponding function values are:
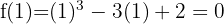
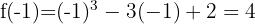
The following figure shows the graph of the given function  .
.


We begin by finding the first and second derivatives of the given function:

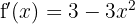
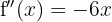
Now let's find the critical points  by solving the equation
by solving the equation  , that is
, that is 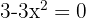 . The solutions to this equation are
. The solutions to this equation are 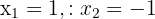 .
.
Finally, we evaluate  at the critical points
at the critical points  and determine whether
and determine whether 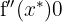 or
or 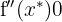 . We have:
. We have:
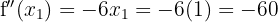
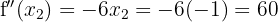
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has a local maximum at
has a local maximum at  and a local minimum at
and a local minimum at  . The corresponding function values are:
. The corresponding function values are:
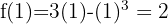
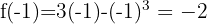
The following figure shows the graph of the given function  .
.


We begin by finding the first and second derivatives of the given function:

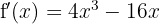
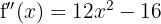
Now let's find the critical points  by solving the equation
by solving the equation  , that is
, that is 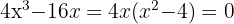 . The solutions to this equation are
. The solutions to this equation are 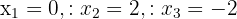 .
.
Finally, we evaluate  at the critical points
at the critical points  and determine whether
and determine whether 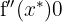 or
or 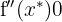 . We have:
. We have:
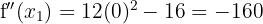
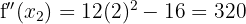
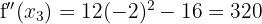
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has a local maximum at
has a local maximum at  and two local minima at
and two local minima at 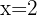 and
and  . The corresponding function values are:
. The corresponding function values are:
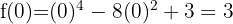
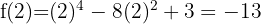
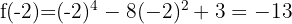
The following figure shows the graph of the given function  .
.

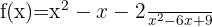
We begin by finding the first and second derivatives of the given function:
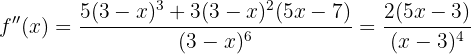
Now let's find the critical point  by solving the equation
by solving the equation  , that is
, that is 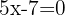 , whose solution is
, whose solution is 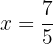 .
.
Finally, we evaluate  at the critical point
at the critical point  and determine whether
and determine whether 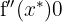 or
or 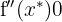 . We have:
. We have:
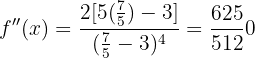
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has a local minimum at
has a local minimum at 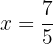 . The corresponding function value is:
. The corresponding function value is:
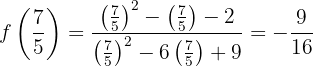
The following figure shows the graph of the given function  .
.

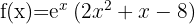
We begin by finding the first and second derivatives of the given function:
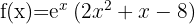
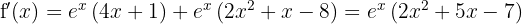

Now let's find the critical points  by solving the equation
by solving the equation  , that is
, that is 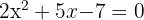 . The solutions to this equation are
. The solutions to this equation are 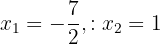 .
.
Finally, we evaluate  at the critical points
at the critical points  and determine whether
and determine whether 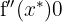 or
or 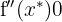 . We have:
. We have:
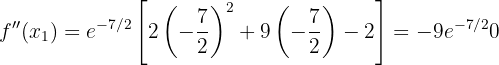
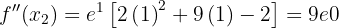
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has a local maximum at
has a local maximum at 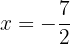 and a local minimum at
and a local minimum at  . The corresponding function values are:
. The corresponding function values are:
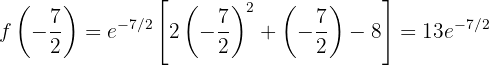
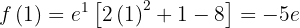
The following figure shows the graph of the given function  .
.

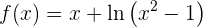
We begin by finding the first and second derivatives of the given function:
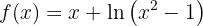
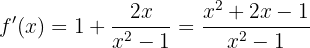
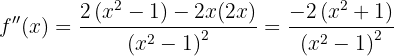
Now let's find the critical points  by solving the equation
by solving the equation  , that is
, that is 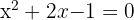 . The solutions to this equation are
. The solutions to this equation are 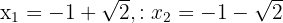 , however, since the domain of the function is
, however, since the domain of the function is 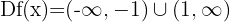 , it is clear that
, it is clear that 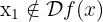 (this is because
(this is because 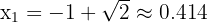 ). Therefore, the only critical point to consider is
). Therefore, the only critical point to consider is  .
.
Finally, we evaluate  at the critical point
at the critical point  and determine whether
and determine whether 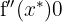 or
or 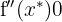 . We have:
. We have:
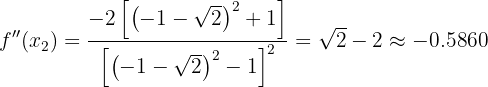
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has a local maximum at
has a local maximum at 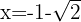 . The corresponding function value is:
. The corresponding function value is:
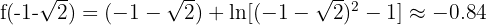
The following figure shows the graph of the given function  .
.

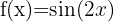
We begin by finding the first and second derivatives of the given function:
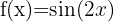
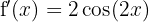
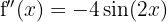
Now let's find the critical points  by solving the equation
by solving the equation  , that is
, that is 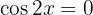 . To do this, let
. To do this, let 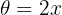 then we have
then we have 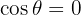 , whose solutions are given by:
, whose solutions are given by:
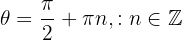
Then, returning to the original variable, we have that the critical points are given by:
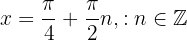
Now we evaluate  at the critical points
at the critical points  and determine whether it is
and determine whether it is 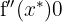 or
or 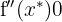 . To do this, let's consider two cases:
. To do this, let's consider two cases:
If 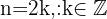 (even), then
(even), then  , so
, so
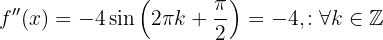
If 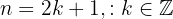 (odd), then
(odd), then 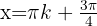 , so
, so
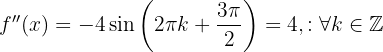
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has its local maxima at
has its local maxima at 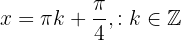 and its local minima at
and its local minima at 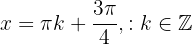 .
.
Furthermore, the corresponding function values are:
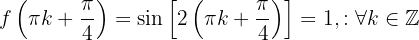
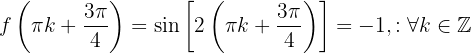
The following figure shows the graph of the given function  .
.

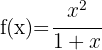
We begin by finding the first and second derivatives of the given function:
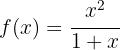
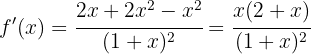
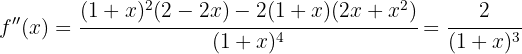
Now we find the critical points  by solving the equation
by solving the equation  .
.
We have:
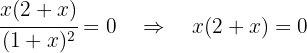
The solutions to this equation are 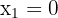 and
and 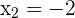 . Thus, we have only two critical points:
. Thus, we have only two critical points:
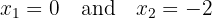
Finally, we evaluate  at the critical point
at the critical point  and determine whether
and determine whether 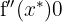 or
or 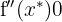 .
.
We have:
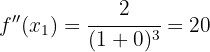
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has a local minimum at the point (0, 0).
has a local minimum at the point (0, 0).
Now we evaluate at the second critical point:
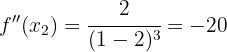
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has a local maximum at the point (-2, -4).
has a local maximum at the point (-2, -4).
The following figure shows the graph of the given function  .
.
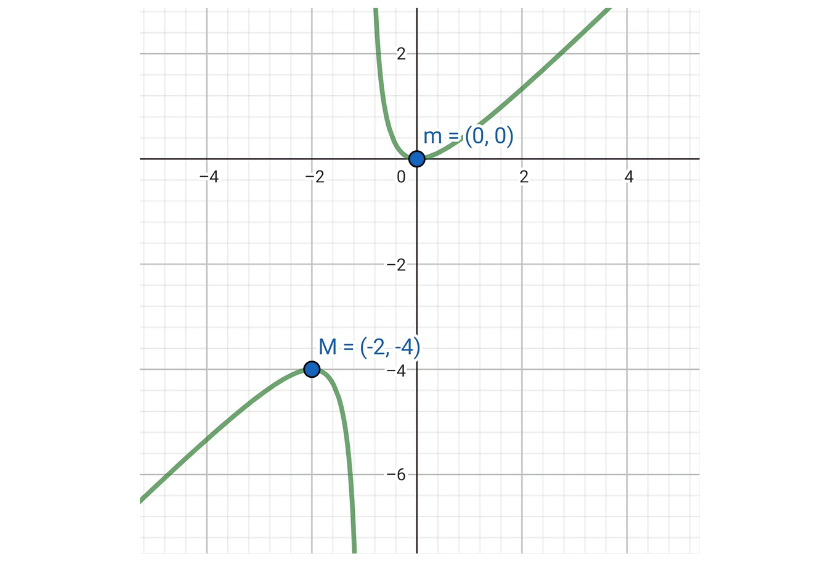
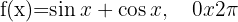
Solution:
We begin by finding the first and second derivatives of the given function:
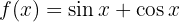
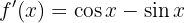
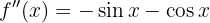
Now we find the critical points  by solving the equation
by solving the equation  .
.
We have:

The solutions to this equation, for 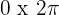 , are
, are 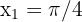 and
and 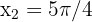 . Thus, we have only two critical points:
. Thus, we have only two critical points:
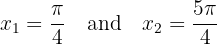
Finally, we evaluate  at the critical point
at the critical point  and determine whether
and determine whether 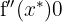 or
or 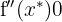 .
.
We have:
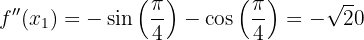
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has a local maximum at the point
has a local maximum at the point 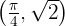 .
.
Now we evaluate at the second critical point:
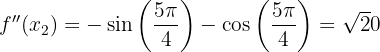
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has a local minimum at the point
has a local minimum at the point 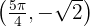 .
.
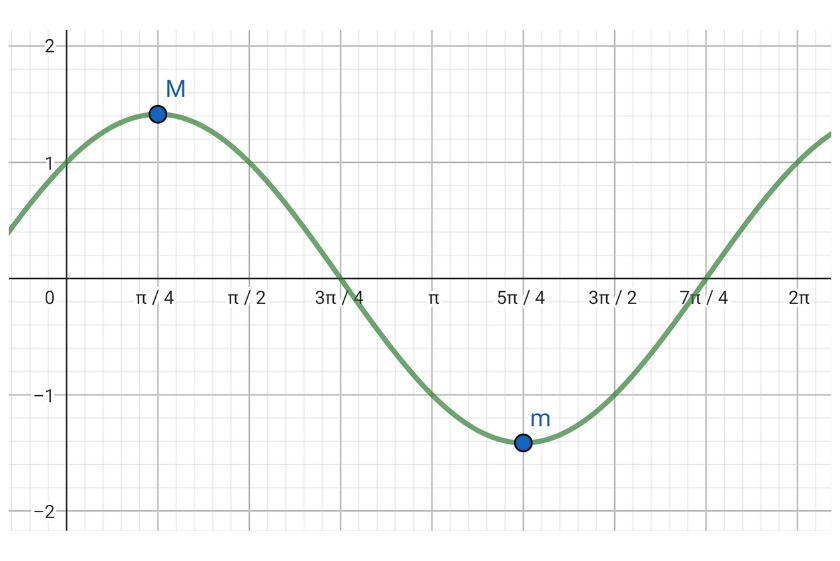
The following figure shows the graph of the given function  .
.
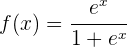
We begin by finding the first and second derivatives of the given function:
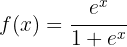
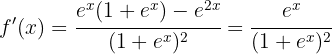
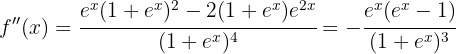
Now we find the critical points  by solving the equation
by solving the equation  .
.
We have:
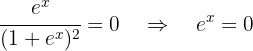
The solution to this equation is 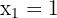 . Thus, we have only one critical point:
. Thus, we have only one critical point:
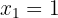
Finally, we evaluate  at the critical point
at the critical point  and determine whether
and determine whether 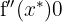 or
or 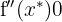 .
.
We have:
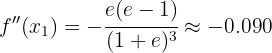
Therefore, by the second derivative test, the function  has a local maximum at the point:
has a local maximum at the point:
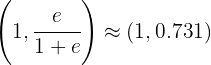
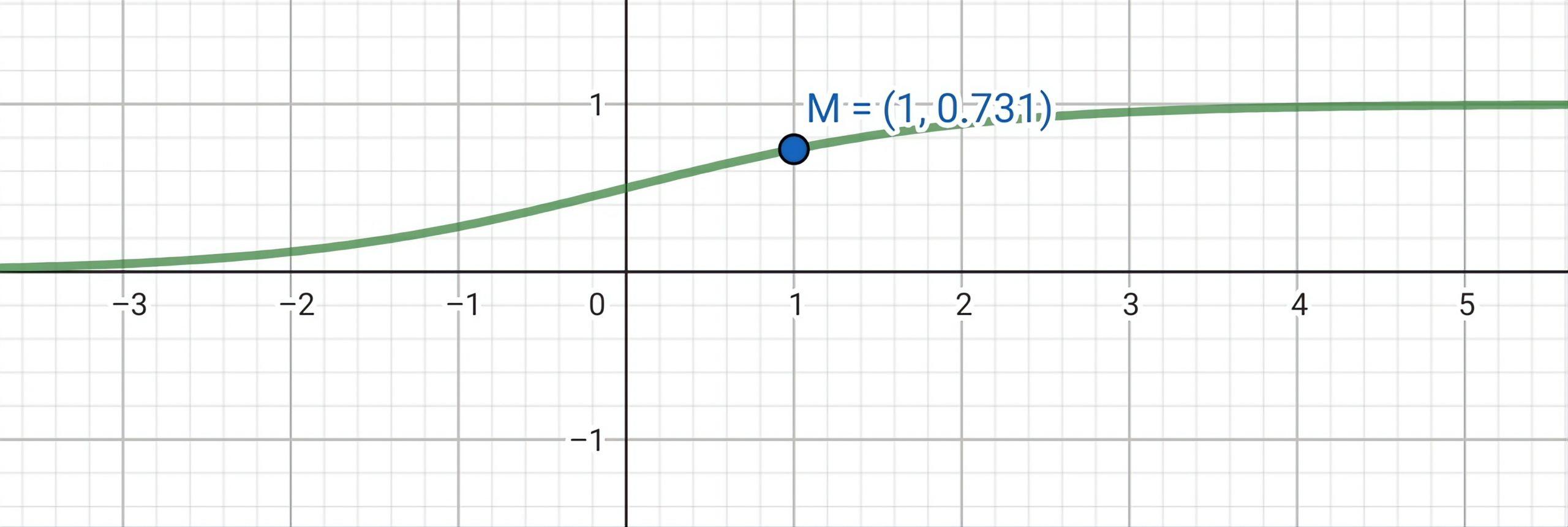
The following figure shows the graph of the given function  .
.
Summarize with AI:


